108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
一种新型的涂在微弧氧化的钛上含有卤代呋喃酮化合物聚(L-乳酸)纳米粒的抗菌涂层的抗菌活性和生物性能
Authors Cheng YC, Zhao XH, Liu XH, Sun WG, Ren HF, Gao B, Wu J
Published Date January 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 727—737
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S75706
Received 12 October 2014, Accepted 26 November 2014, Published 19 January 2015
Abstract: Titanium implants have been widely used for many medical applications,
but bacterial infection after implant surgery remains one of the most common
and intractable complications. To this end, long-term antibacterial ability of
the implant surface is highly desirable to prevent implant-associated infection.
In this study, a novel antibacterial coating containing a new antibacterial
agent, (Z-)-4-bromo-5-(bromomethylene)-2(5H)-furanone loaded poly(L-lactic
acid) nanoparticles, was fabricated on microarc-oxidized titanium for this
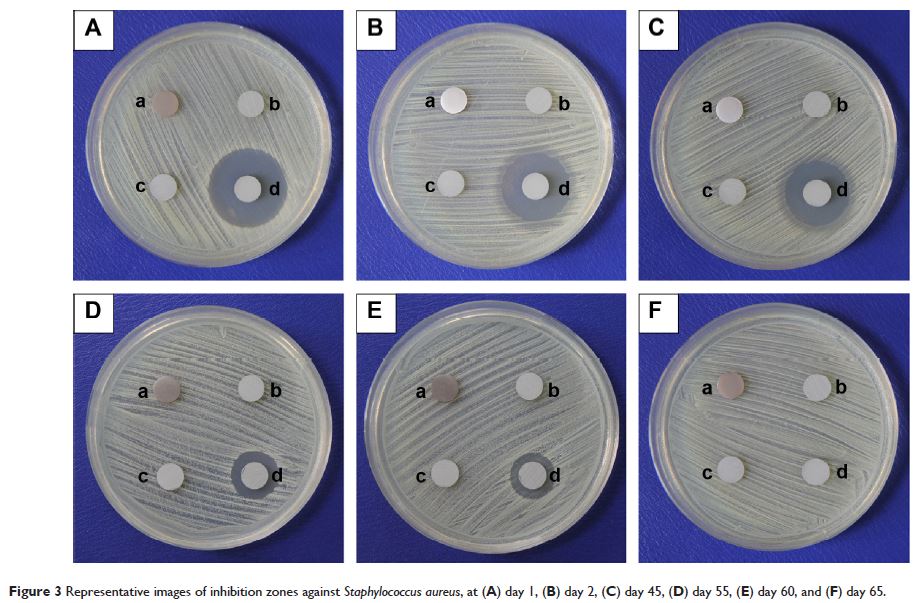
purpose. The antibacterial coating produced a unique inhibition zone against Staphylococcus aureus throughout a
60-day study period, which is normally long enough to prevent the infection
around implants in the early and intermediate stages. The antibacterial rate
for adherent S. aureus was about 100% in the
first 10 days and constantly remained over 90% in the following 20 days.
Fluorescence staining of adherent S. aureus also
confirmed the excellent antibacterial ability of the antibacterial coating.
Moreover, in vitro experiments showed an enhanced osteoblast adhesion and
proliferation on the antibacterial coating, and more notable cell spread was
observed at the early stage. It is therefore concluded that the fabricated
antibacterial coating, which exhibits relatively long-term antibacterial
ability and excellent biological performance, is a potential and promising
strategy to prevent implant-associated infection.
Keywords: microarc oxidation, osteoblasts
Keywords: microarc oxidation, osteoblasts