108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氧化还原响应和 pH 敏感性纳米颗粒增强厄洛替尼体内治疗肺癌的稳定性和抗癌能力
Authors Tan S, Wang G
Received 11 September 2017
Accepted for publication 3 November 2017
Published 8 December 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 3519—3529
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S151422
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Purpose: Erlotinib
(ETB) is a well-established therapeutic for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
To overcome drug resistance and severe toxicities in the clinical application,
redox-responsive and pH-sensitive nanoparticle drug delivery systems were
designed for the encapsulation of ETB.
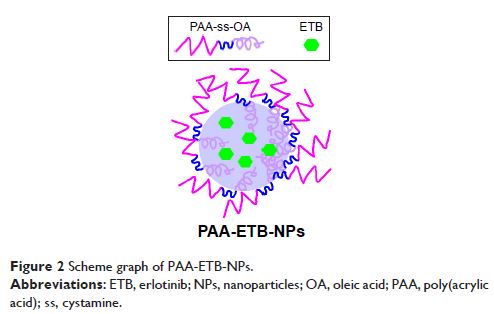
Methods: Poly(acrylic acid)-cystamine-oleic acid (PAA-ss-OA) was
synthesized. PAA-ss-OA-modified ETB-loaded lipid nanoparticles (PAA-ETB-NPs)
were prepared using the emulsification and solvent evaporation method. The
tumor inhibition efficacy of PAA-ETB-NPs was compared with that of ETB-loaded
lipid nanoparticles (ETB-NPs) and free ETB anticancer drugs in tumor-bearing
mice.
Results: PAA-ETB-NPs had a size of 170 nm, with a zeta potential of -32 mV.
The encapsulation efficiency and drug loading capacity of PAA-ETB-NPs were over
85% and 2.6%, respectively. In vitro cytotoxicity of ETB-NPs were higher than
that of ETB solution. The cytotoxicity of PAA-ETB-NPs was the highest. The in
vivo tumor growth inhibition by PAA-ETB-NP treatment was significantly higher
than that by ETB-NPs and ETB solution. No obvious weight loss was observed in any
of the treatment groups, indicating that all the treatments were well
tolerated.
Conclusion: PAA-ETB-NPs could enhance the stability and anti-cancer ability of
ETB to treat lung cancer and are a promising drug delivery system for lung
cancer treatment.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor, kinase inhibitor, pH-sensitive,
redox-responsive, poly(acrylic acid)