108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

食管癌位置转移和总体生存率:基于人群的研究
Authors Wu SG, Zhang WW, He ZY, Sun JY, Chen YX, Guo L
Received 30 August 2017
Accepted for publication 31 October 2017
Published 6 December 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 781—788
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S150350
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
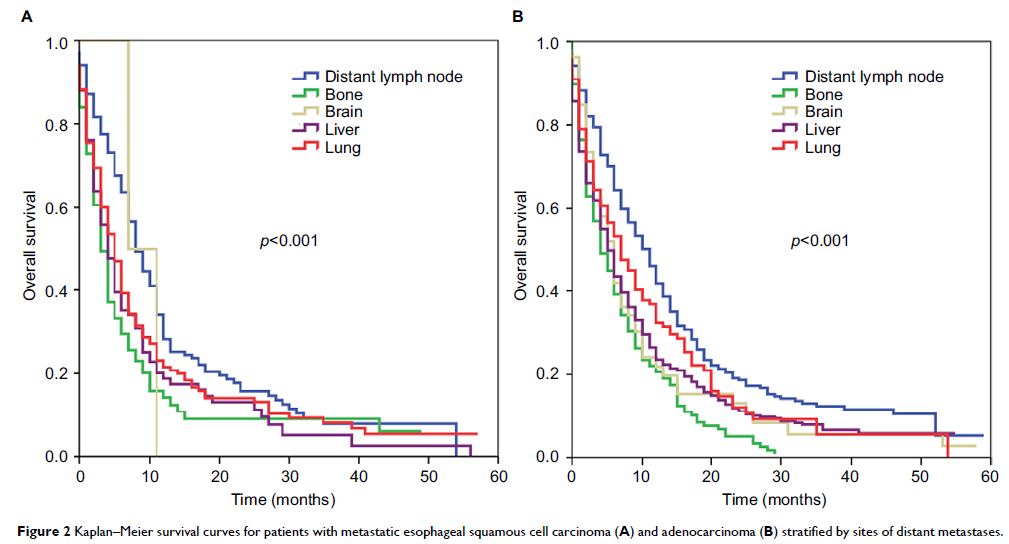
Background: There are few population-based studies of the sites of distant
metastasis (DM) and survival from esophageal cancer (EC). The aim of this study
was to assess the patterns and survival outcomes for site-specific DM from EC
using a population-based approach.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with de novo stage IV EC
between 2010 and 2014 were identified from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and
End Results program database. Overall survival (OS) was compared according to
the site of DM.
Results: We included 3218 patients in this study; the
most common site of DM was the liver, followed by distant lymph nodes, lung,
bone and brain. Median OS for patients with liver, distant lymph node, lung,
bone, and brain metastases was 5, 10, 6, 4, and 6 months, respectively (p <0.001). Site and number of
distant metastases were independent prognostic factors for OS. In patients with
a single site of DM, using liver metastases as reference, OS was lower for bone
metastases (p =0.026) and higher for distant
lymph node metastases (p =0.008), while
brain (p =0.653) or lung (p =0.081) metastases had similar OS
compared with liver metastases. Similar site-specific survival differences were
observed in the subgroup with esophageal adenocarcinoma. However, distant lymph
node metastases was associated with better survival (p =0.002) compared to liver, bone,
or lung metastases in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Conclusion: Site of metastasis affects survival in
metastatic EC; OS was worst for bone metastases and greatest for distant lymph
node metastases.
Keywords: esophageal
cancer, SEER, bone metastases, liver metastases, lung metastases, brain
metastases