108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

普鲁兰包裹的磷脂和普卢兰尼克 F68 复合纳米粒子装载 IR780 和紫杉醇,用于在光热疗法/光动力疗法和化学疗法相结合中治疗肝细胞癌
Authors Wang D, Zhang SP, Zhang T, Wan GY, Chen BW, Xiong QQ, Zhang J, Zhang WX, Wang YS
Received 28 July 2017
Accepted for publication 22 October 2017
Published 5 December 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 8649—8670
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S147591
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
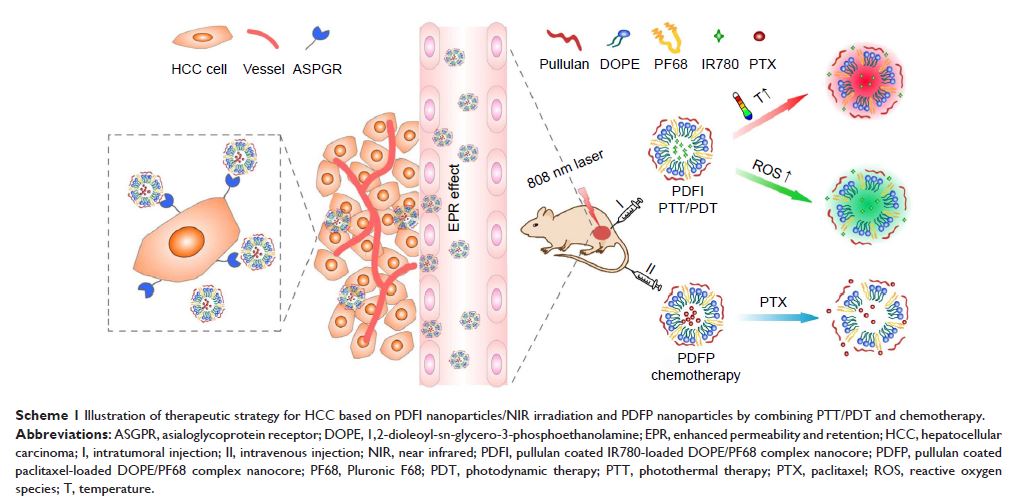
Abstract: IR780,
a near-infrared dye, can also be used as a photosensitizer both for
photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT). In this study, we
designed a simple but effective nanoparticle system for carrying IR780 and
paclitaxel, thus hoping to combine PTT/PDT and chemotherapy to treat
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This nanosystem, named PDF nanoparticles,
consisted of phospholipid/Pluronic F68 complex nanocores and pullulan shells.
IR780 and paclitaxel were loaded separately into PDF nanoparticles to form PDFI
and PDFP nanoparticles, which had regular sphere shapes and relatively small
sizes. Upon near-infrared laser irradiation at 808 nm, PDFI nanoparticles
showed strong PTT/PDT efficacy both in vitro and in vivo. In MHCC-97H cells,
the combined treatment of PDFI nanoparticles/laser irradiation and PDFP
nanoparticles exhibited significant synergistic effects on inhibiting cell
proliferation and inducing cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase.
In MHCC-97H tumor-bearing mice, PDFI nanoparticles exhibited excellent HCC-targeting
and accumulating capability after intravenous injection. Furthermore, the
combined treatment of PDFI nanoparticles/laser irradiation and PDFP
nanoparticles also effectively inhibited the tumor growth and the tumor
angiogenesis in MHCC-97H tumor-bearing mice. In summary, we put forward a
therapeutic strategy for HCC treatment by combining PTT/PDT and chemotherapy.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, IR780, paclitaxel, combination therapy,
nanoparticle