108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
胃癌组织中用于 CD146 的 MR/NIRF 成像的生物功能化致密二氧化硅纳米粒子
Authors Wang P, Qu Y, Li C, Yin L, Shen C, Chen W, Yang S, Bian X, Fang D
Published Date January 2015 Volume 2015:10 Pages 749—763
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S62837
Received 21 February 2014, Accepted 5 July 2014, Published 20 January 2015
Purpose: Nano dense-silica (d SiO2)
has many advantages such as adjustable core–shell structure, multiple drug
delivery, and controllable release behavior. Improving the gastric
tumor-specific targeting efficiency based on the development of various
strategies is crucial for anti-cancer drug delivery systems.
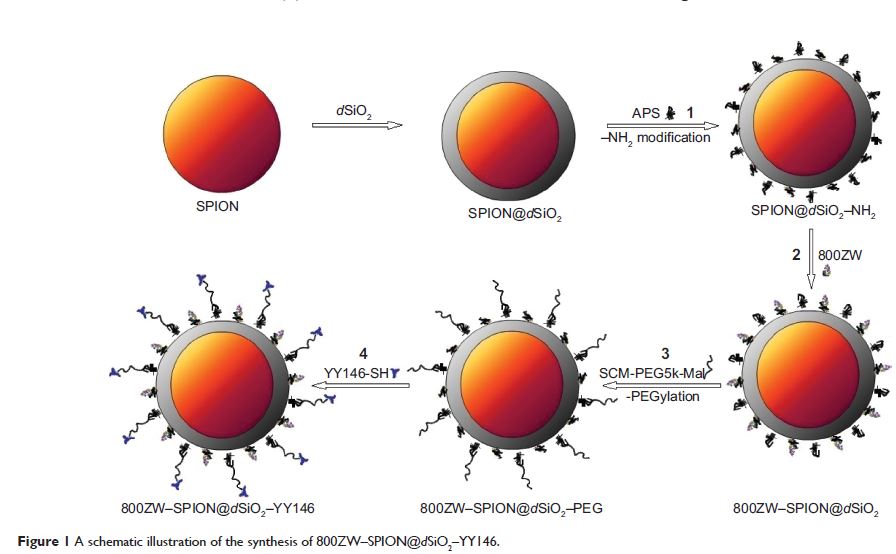
Methods: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) were coated with d SiO2 as core–shell nanoparticles, and labeled with near infra-red fluorescence (NIRF) dye 800ZW (excitation wavelength: 778 nm/emission wavelength: 806 nm) and anti-CD146 monoclonal antibody YY146 for magnetic resonance (MR)/NIRF imaging study in xenograft gastric cancer model. The morphology and the size of pre- and postlabeling SPION@d SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles were characterized using transmission electron microscopy. Iron content in SPION@d SiO2 nanoparticles was measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Fluorescence microscopy and fluorescence-activated cell sorter studies were carried out to confirm the binding specificity of YY146 and 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 on MKN45 cells. In vivo and in vitro NIRF imaging, control (nanoparticles only) and blocking studies, and histology were executed on MKN45 tumor-bearing nude mice to estimate the affinity of 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 to target tumor CD146.
Results: 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 nanoparticles were uniformly spherical in shape and dispersed evenly in a cell culture medium. The diameter of the nanoparticle was 20–30 nm with 15 nm SPION core and ~10 nm SiO2 shell, and the final concentration was 1.7 nmol/mL. Transverse relaxivity of SPION@d SiO2 dispersed in water was measured to be 110.57 mM-1·s-1. Fluorescence activated cell sorter analysis of the nanoparticles in MKN45 cells showed 14-fold binding of 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 more than the control group 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2. Series of NIRF imaging post intravenous injection of 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 demonstrated that the MKN45 xenograft tumor model could be clearly identified as early as a time point of 30 minutes postinjection. Quantitative analysis revealed that the tumor uptake peaked at 24 hours postinjection.
Conclusion: This is the first successful study of functional nanoparticles for MR/NIRF imaging of cell surface glycoprotein CD146 in gastric cancer model. Our results suggest that 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 nanoparticles will be applicable in tumor for image-guided therapy/surgery.
Keywords: SPION, nanotechnology, EMT, SPION@d SiO2, xenograft, gastric cancer
Methods: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION) were coated with d SiO2 as core–shell nanoparticles, and labeled with near infra-red fluorescence (NIRF) dye 800ZW (excitation wavelength: 778 nm/emission wavelength: 806 nm) and anti-CD146 monoclonal antibody YY146 for magnetic resonance (MR)/NIRF imaging study in xenograft gastric cancer model. The morphology and the size of pre- and postlabeling SPION@d SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles were characterized using transmission electron microscopy. Iron content in SPION@d SiO2 nanoparticles was measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry. Fluorescence microscopy and fluorescence-activated cell sorter studies were carried out to confirm the binding specificity of YY146 and 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 on MKN45 cells. In vivo and in vitro NIRF imaging, control (nanoparticles only) and blocking studies, and histology were executed on MKN45 tumor-bearing nude mice to estimate the affinity of 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 to target tumor CD146.
Results: 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 nanoparticles were uniformly spherical in shape and dispersed evenly in a cell culture medium. The diameter of the nanoparticle was 20–30 nm with 15 nm SPION core and ~10 nm SiO2 shell, and the final concentration was 1.7 nmol/mL. Transverse relaxivity of SPION@d SiO2 dispersed in water was measured to be 110.57 mM-1·s-1. Fluorescence activated cell sorter analysis of the nanoparticles in MKN45 cells showed 14-fold binding of 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 more than the control group 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2. Series of NIRF imaging post intravenous injection of 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 demonstrated that the MKN45 xenograft tumor model could be clearly identified as early as a time point of 30 minutes postinjection. Quantitative analysis revealed that the tumor uptake peaked at 24 hours postinjection.
Conclusion: This is the first successful study of functional nanoparticles for MR/NIRF imaging of cell surface glycoprotein CD146 in gastric cancer model. Our results suggest that 800ZW–SPION@d SiO2–YY146 nanoparticles will be applicable in tumor for image-guided therapy/surgery.
Keywords: SPION, nanotechnology, EMT, SPION@d SiO2, xenograft, gastric cancer