108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

更正启事 — 维持治疗在老年非小细胞肺癌患者治疗中的作用:随机对照试验的荟萃分析
Authors Zhang L, Gao S, He J
Received 28 June 2017
Accepted for publication 5 August 2017
Published 1 December 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 3435—3440
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S145025
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Purpose: Maintenance therapy is an effective treatment strategy for
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We aim to investigate whether age
would affect the efficacy of maintenance therapy in the treatment of advanced
NSCLC.
Materials and methods: Relevant trials were identified by searching
electronic databases and conference meetings. Prospective randomized controlled
trials assessing maintenance therapy in elderly patients with advanced NSCLC
were included. Outcomes of interest included overall survival (OS) and
progression-free survival (PFS) in elderly patients with advanced NSCLC.
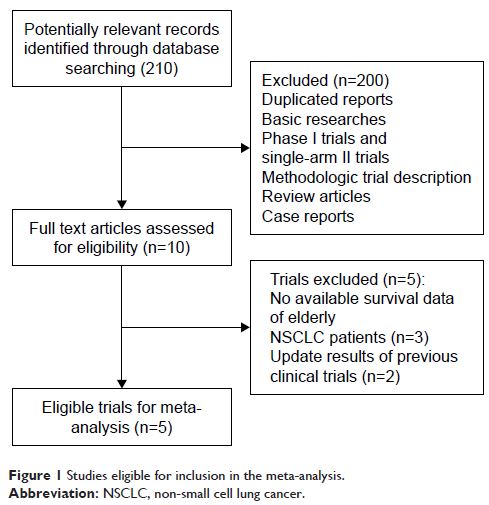
Results: A total of 2,724 patients from 5 randomized
controlled trials were included for analysis, with 897 patients aged ≥65 years
and 1,577 patients aged <65 years. Single-agent maintenance therapy in
elderly patients significantly improved PFS (hazard ratio [HR] 0.65, 95% CI: 0.43–0.98, p =0.04) and OS (HR 0.81, 95% CI:
0.68–0.97, p =0.024) when compared with
placebo. In addition, doublet maintenance therapy significantly improved PFS
(HR 0.81, 95% CI: 0.68–0.97, p =0.024) in
comparison with single-agent maintenance therapy. However, doublet maintenance
did not improve OS in comparison with single-agent maintenance therapy (HR
1.05, 95% CI: 0.60–1.83, p =0.86).
Conclusions: The findings of this study suggest that
single-agent maintenance therapy in elderly patients with advanced NSCLC offers
an improved PFS and OS when compared with placebo. Further trials are
recommended to clearly investigate the efficacy of combination maintenance
therapy for advanced NSCLC in this setting.
Keywords: non-small-cell
lung cancer, maintenance therapy, elderly, meta-analysis, lung neoplasm, older,
systematic review
*在 3435 页,第一作者的名字被错误地列为 Liangzhe Zhang。 他的正确名字应该是:Liangze Zhang 。
请点击这里查看详细更正启事