108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

髓内钉、锁定钢板和保守治疗对老年人肱骨近端骨折移位的疗效比较
Authors Ge W, Sun Q, Li G, Lu G, Cai M, Li S
Received 15 June 2017
Accepted for publication 5 November 2017
Published 29 November 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2047—2054
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S144084
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Wu
Purpose: The incidence of proximal humeral fractures is high in the elderly,
and the superior management of these fractures remains a controversy. The study
aims to compare clinical outcomes of intramedullary nails, locking plates and
conservative treatment for the management of displaced proximal humeral
fractures in the elderly.
Patients and methods: In this prospective study, a total of 198
patients with 2- or 3-part proximal humeral fractures who received fixation of
locking plates or intramedullary nails or conservative treatment were included.
The primary outcome was the 24-month Constant–Murley score. The secondary
outcomes included the American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) scores, the
visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, shoulder range of motion and
complication rate.
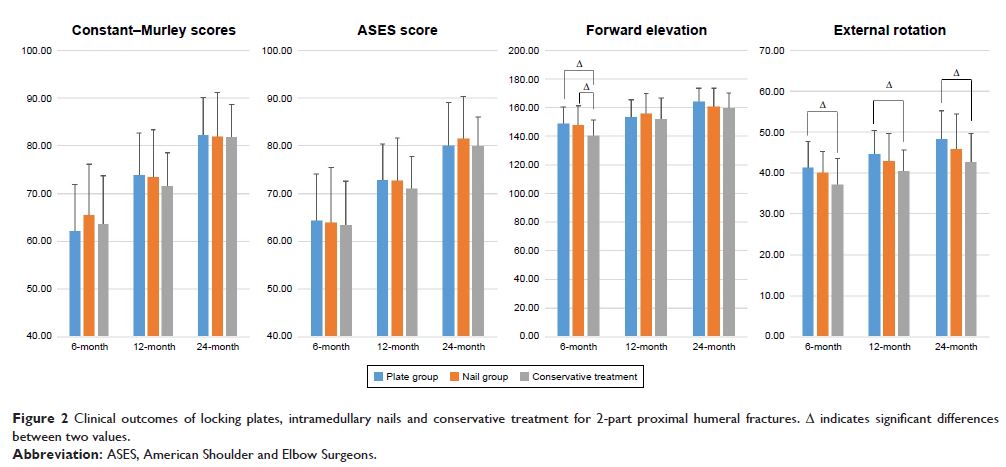
Results: There were no statistically significant differences in
the Constant–Murley scores and ASES scores among the plate group, the nail
group and the conservative group for 2-part fractures. For 3-part fractures,
Constant–Murley scores and ASES scores were lower in the conservative group compared
with those in the plate group and the nail group. Besides, the conservative
group showed a significantly lower external rotation during follow-ups. The
complication rate was comparable among the plate group, the nail group and the
conservative group for both 2-part and 3-part fractures.
Conclusion: Similar satisfactory functional outcomes can be
achieved with the locking plates, intramedullary nails or conservative
treatment for 2-part proximal humeral fractures in the elderly. The advantages
in functional outcomes favor locking plates and intramedullary nails in the
management of 3-part proximal humeral fractures.
Keywords: proximal
humeral fractures, intramedullary nails, locking plates, conservative
treatment, the elderly