108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:MicroRNA-211 通过靶向 MxA 促进非小细胞肺癌的增殖和侵袭
Authors Kang M, Shi J, Peng N, He S
Received 2 June 2017
Accepted for publication 1 October 2017
Published 28 November 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5667—5675
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S143084
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Dekuang Zhao
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
***本文章已被撤回***
Abstract: Recent studies have shown that microRNAs play a pivotal role in
the pathogenesis of cancer. In our current study, the expression levels of
microRNA-211 (miR-211) were measured in human non-small-cell lung cancer
(NSCLC) tissues and cell lines. We found that miR-211 expression levels were
increased in NSCLC tissues and cell lines and that the overexpression of
miR-211 promotes cell proliferation and invasion. Using bioinformatics, we
demonstrated that miR-211 binds to the 3'-untranslated region of MxA and overexpression
of miR-211 suppresses the expression of MxA at both the transcriptional and
translational levels in NSCLC cell lines. Furthermore, knockdown of MxA
increased the proliferation and invasion of NSCLC cell lines in vitro. High
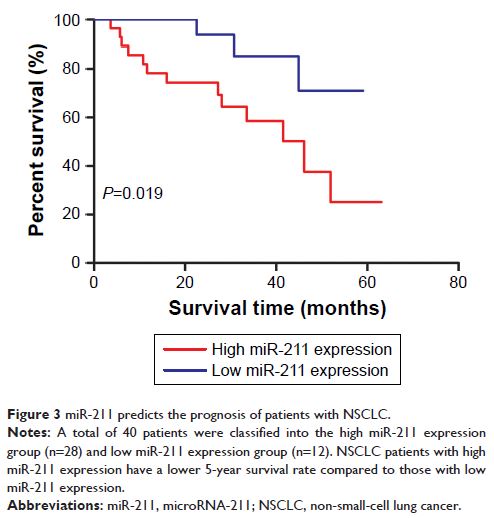
levels of miR-211 expression were associated with a shorter survival time in
patients with NSCLC. Taken together, these results suggest that miR-211
promotes tumor proliferation and invasion by regulating MxA expression in
NSCLC. This study provides insights into molecular mechanisms of
miR-211-mediated tumorigenesis and oncogenesis.
Keywords: miR-211, MxA,
non-small-cell lung cancer, proliferation, invasion