108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

循环血中长链非编码 RNA PCAT6 在非小细胞肺癌诊断中的意义
Authors Wan L, Zhang L, Fan K, Wang JJ
Received 17 August 2017
Accepted for publication 11 October 2017
Published 28 November 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5695—5702
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S149314
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Aim: We
have previously shown that the long noncoding RNA prostate cancer-associated
transcript 6 (PCAT6) promoted the proliferation and invasion of lung
adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cells. In this study, the diagnostic significance of
tissue and serum PCAT6 was evaluated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Materials and
methods: Tissue expression of PCAT6 was
systematically evaluated in five Gene Expression Omnibus datasets (GSE19804,
GSE18842, GSE30219, GSE19188, and GSE27262). Circulating and tissue expressions
of PCAT6 were detected by quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain
reaction in NSCLC patients from Union Hospital.
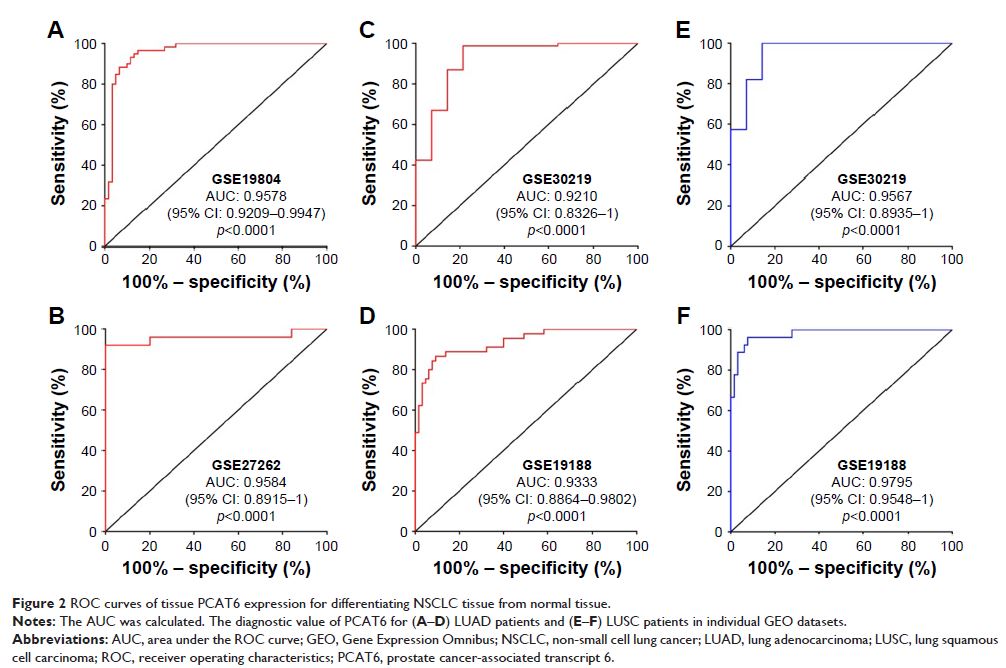
Results: PCAT6 was significantly increased in lung cancer tissues and could be
used to distinguish LUAD from adjacent normal tissues with an area under the
receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.9210 (p <0.0001; sensitivity, 98.82%;
specificity, 78.57%) in GSE30219, 0.9333 (p <0.0001;
sensitivity, 86.67%; specificity, 90.77%) in GSE19188, 0.9584 (p <0.0001; sensitivity, 92.00%;
specificity, 96.00%) in GSE27262, and 0.9574 (p <0.0001;
sensitivity, 95.89%; specificity, 87.67%) in patients from Union Hospital. As
for lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), the AUC of PCAT6 was 0.9567 (p <0.0001; sensitivity, 100%;
specificity, 85.71%) in GSE30219, 0.9795 (p <0.0001;
sensitivity, 96.30%; specificity, 92.31%) in GSE19188, and 0.9942 (p <0.0001; sensitivity, 100%;
specificity, 98.04%) in patients from Union Hospital. We further noticed that
the plasma levels of PCAT6 were significantly increased in 73 LUAD and 51 LUSC
patients compared with 39 healthy controls (p <0.0001). The
AUC of circulating PCAT6 was 0.9213 (p <0.0001;
sensitivity, 87.67%; specificity, 97.44%) in LUAD and 0.9583 (p <0.0001; sensitivity, 94.12%;
specificity, 100%) in LUSC.
Conclusion: Together with our previous findings, our results suggest that PCAT6
could be used as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in NSCLC.
Keywords: lncRNAs, PCAT6, diagnosis, lung adenocarcinoma, lung squamous cell
carcinoma