108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Ki-67/MIB-1 在肾细胞癌中的表达及临床病理价值 - 基于对 4,579 名患者的研究荟萃分析
Authors Wang Z, Xie H, Guo LP, Cai QL, Shang ZQ, Jiang N, Niu YJ
Received 12 May 2017
Accepted for publication 9 October 2017
Published 21 November 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 679—689
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S141670
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Background: Previous
studies have investigated the prognostic significance of Ki-67/MIB-1 expression
in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), however, the reports are controversial and
inconsistent. This study aimed to investigate Ki-67/MIB-1 expression in RCC and
its correlation with prognosis and clinicopathological features.
Methods: We searched relevant studies that reported associations between
Ki-67/MIB-1 expression and prognosis in RCC from PubMed, Embase, Web of Science,
and Cochrane Library studies published until April 14, 2017. Hazard ratios
(HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were extracted from eligible studies.
Fixed and random effects models were used to calculate pooled HRs and 95% CIs
according to heterogeneity.
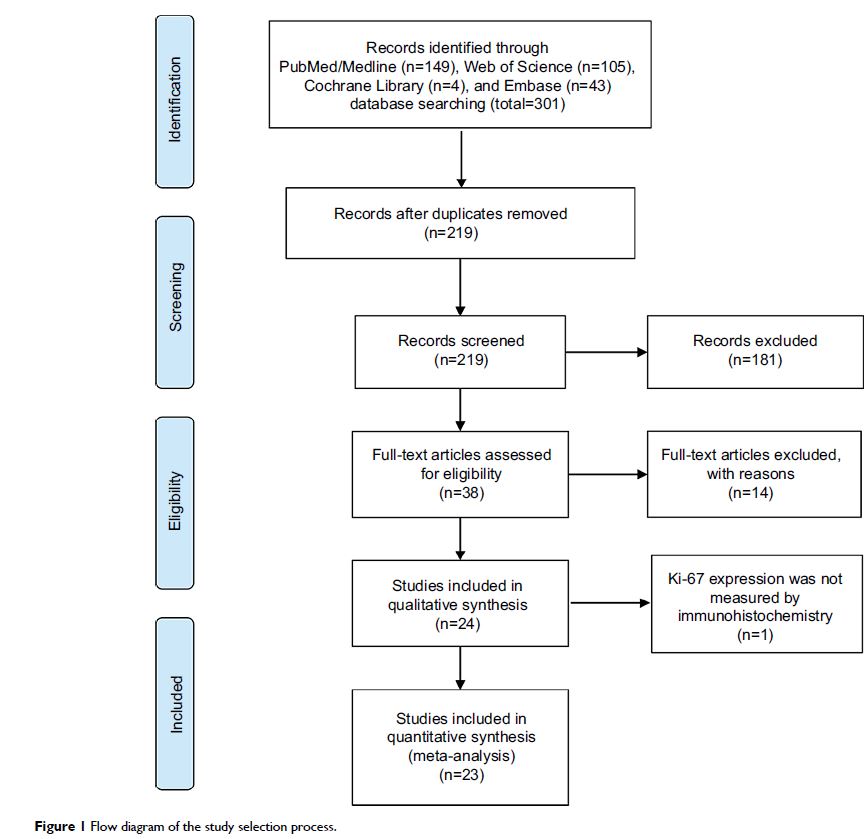
Results: A total of 4579 participants from 23 eligible studies were
included in this analysis. The results showed that Ki-67/MIB-1 expression was
associated with poor overall survival (HR=2.06, 95% CI: 1.64–2.57) and cancer
specific survival (HR=2.01, 95% CI: 1.66–2.44). In addition, Ki-67/MIB-1
expression was also correlated with TNM stage (III/IV vs I/II: OR=1.92, 95% CI:
1.61–2.28), pathological T stage (pT3/pT4 vs pT1/pT2: OR=1.56, 95% CI:
1.21–2.02), distant metastasis (M1 vs M0: OR=1.81, 95% CI: 1.34–2.43), and
Fuhrman grade (III/IV vs I/II: OR=1.94, 95% CI: 1.21–3.10).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that the presence of high Ki-67/MIB-1
expression and advanced clinicopathological features were correlated with poor
prognosis in RCC patients.
Keywords: Ki-67/MIB-1, renal cell carcinoma, prognosis, meta-analysis