108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
对中国西北地区高血压病患者进行出院后的药物依从性和高血压知识评估
Authors Pan JJ, Lei T, Hu B, Li QG
Received 28 July 2017
Accepted for publication 5 October 2017
Published 20 November 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1915—1922
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S147605
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Objectives: The aims of
this study were to assess the knowledge of hypertension (HTN) and investigate
risk factors associated with medication adherence among hypertensive stroke
patients after discharge in the northwestern China.
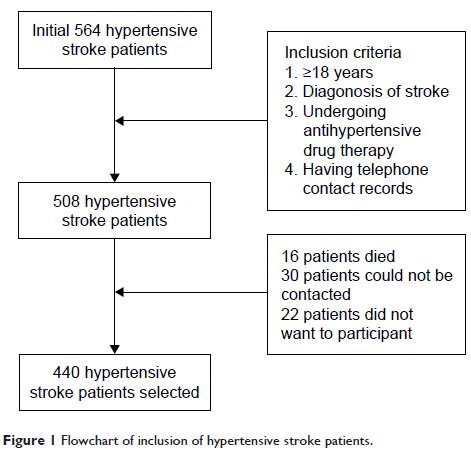
Patients and methods: A cross-sectional study involving 440 Chinese hypertensive stroke patients was conducted in a tertiary hospital in Xi’an, China. Data were collected by telephone interviews and patients’ medical records.
Results: It was found that 35.23% of patients were compliant with their antihypertensive drug treatments, and 42.95%, 52.27% and 4.77% of patients had poor, moderate and adequate knowledge of HTN, respectively. Gender, blood pressure (BP) categories, BP monitoring and HTN knowledge were independently associated with antihypertensive medication adherence.
Conclusion: The medication adherence among hypertensive stroke patients in northwestern China was poor. Knowledge of HTN was suboptimal. More attention and effective strategies should be designed to the factors affecting medication adherence. As knowledge positively affects medication adherence, clinical pharmacists should play an important role in patients’ medication education.
Keywords: medication adherence, knowledge, hypertension, stroke, clinical pharmacist, China
Patients and methods: A cross-sectional study involving 440 Chinese hypertensive stroke patients was conducted in a tertiary hospital in Xi’an, China. Data were collected by telephone interviews and patients’ medical records.
Results: It was found that 35.23% of patients were compliant with their antihypertensive drug treatments, and 42.95%, 52.27% and 4.77% of patients had poor, moderate and adequate knowledge of HTN, respectively. Gender, blood pressure (BP) categories, BP monitoring and HTN knowledge were independently associated with antihypertensive medication adherence.
Conclusion: The medication adherence among hypertensive stroke patients in northwestern China was poor. Knowledge of HTN was suboptimal. More attention and effective strategies should be designed to the factors affecting medication adherence. As knowledge positively affects medication adherence, clinical pharmacists should play an important role in patients’ medication education.
Keywords: medication adherence, knowledge, hypertension, stroke, clinical pharmacist, China