108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

局部晚期鼻咽癌细胞的 PD-L1 表达
Authors Zheng L, Cao C, Cheng G, Hu Q, Chen X
Received 19 September 2017
Accepted for publication 17 October 2017
Published 16 November 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5483—5487
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S152007
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Background and
objective: The aim of this study was to
evaluate the expression of cytomembranic programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and
its clinical significance in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma
(NPC).
Patients and methods: Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue biopsies from 85 patients
with histological diagnosis of locoregionally advanced NPC treated with radical
intensity-modulated radiotherapy and concurrent cisplatin-based chemotherapy
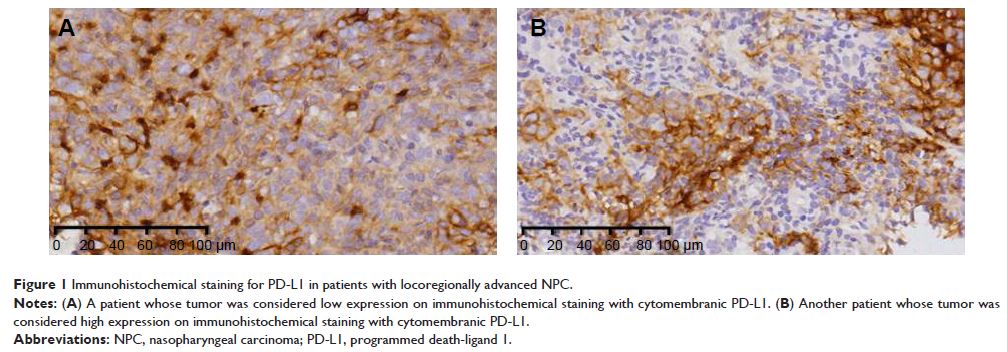
were studied. By using immunohistochemistry staining, expressions of
cytomembranic PD-L1 on tumor cells were detected.
Results: After a median follow-up duration of 65.8 months, 7 (8.2%), 5 (5.9%),
and 5 (5.9%) patients suffered from local failure, regional failure, and
distant metastases, respectively. The 5-year local failure-free survival,
regional failure-free survival, distant failure-free survival, and overall
survival (OS) rates were 90.9%, 94.8%, 94.0%, and 92.2%, respectively. Our
results revealed that a high expression of cytomembranic PD-L1 was correlated
with shorter OS (5y-OS: 82.5% vs 97.6%, P =0.022). In the
multivariate analysis, only the cytomembranic PD-L1 was an independent
prognostic factor for OS (hazard ratio: 6.176, 95% confidence interval,
1.166–32.710, P =0.032).
Conclusion: Cytomembranic PD-L1 expression levels correlated with OS in
locoregionally advanced NPC. Agreement between different methods is needed for
further application of PD-L1 biomarker assays in NPC.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, programmed death-ligand 1, PD-L1, prognosis,
overall survival
摘要视频链接:Cytomembranic PD-L1
expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma