108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:姜黄素通过抑制 PI3K/AKT 和 NF-κB/COX-2 信号通路增强 ACNU 对胶质母细胞瘤的有效抗肿瘤活性
Authors Zhao J, Zhu J, Lv X, Xing J, Liu S, Chen C, Xu Y
Received 22 August 2017
Accepted for publication 3 October 2017
Published 15 November 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5471—5482
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S149708
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jia Fan
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
***本文章已被撤回***
Abstract: Glioblastoma
(GBM) is a highly invasive and challenging primary tumor of the central nervous
system (CNS), and currently available treatments provide limited benefits to
patients with this disease. Therefore, the development of novel therapeutic
targets and effective treatment strategies is essential. Nimustine
hydrochloride (ACNU) is widely used as the standard chemotherapeutic agent and
is frequently administered together with other chemotherapeutic agents in clinical
studies. Curcumin, a natural polyphenolic compound, could potentially be
combined with chemotherapeutics for cancer treatment; however, there are no
reports of studies where ACNU and curcumin were combined for GBM treatment, and
the mechanisms underlying their activity remain poorly understood. In the
present study, we investigated the effects of combined treatment with curcumin
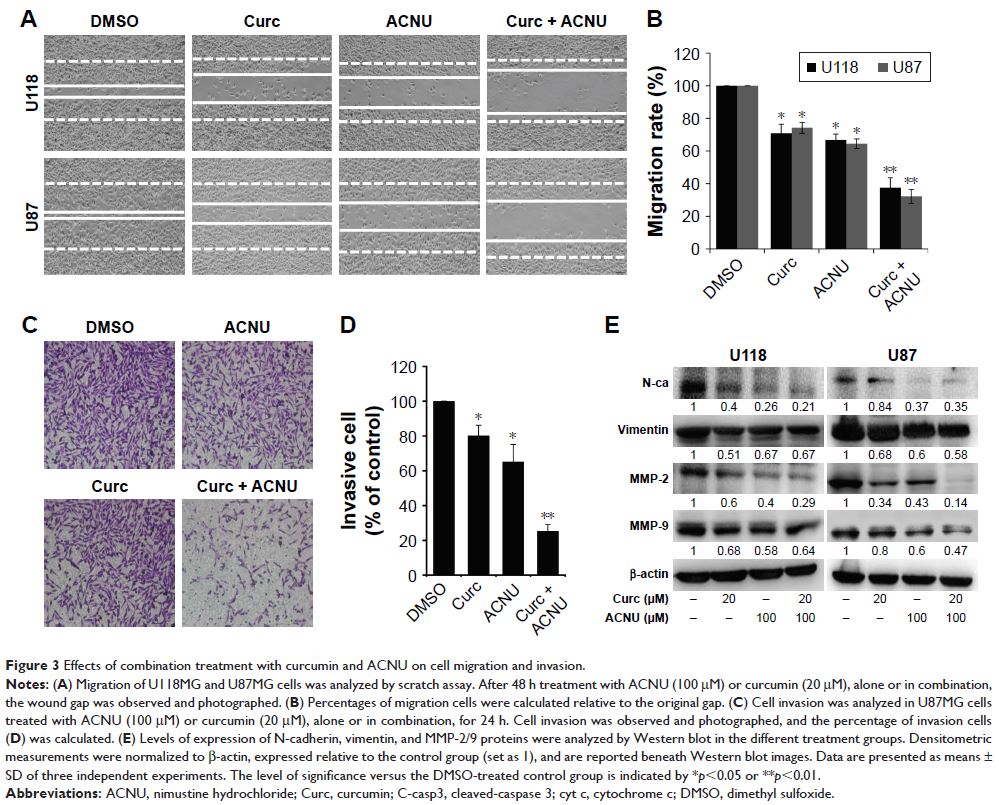
and ACNU on GBM cells and found that it significantly enhanced the inhibition
of cell proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion. In addition,
co-treatment with curcumin increased ACNU-induced apoptosis through enhancing
the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondrial intermembrane space into the
cytosol. Further, curcumin and ACNU acted synergistically in their antitumor
effects by targeting N-cadherin/MMP2/9, PI3K/AKT, and NF-κB/COX-2 signaling.
These results indicate that curcumin can enhance the anti-proliferation,
anti-migration, and proapoptotic activities of ACNU against GBM, and provide
strong evidence that combined treatment with curcumin and ACNU has the
potential to be an effective therapeutic option for GBM.