108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
手术治疗转移性膀胱癌的部位特异性转移的预后价值和治疗作用:一项基于人群的研究
Authors Dong F, Shen Y, Gao F, Xu T, Wang X, Zhang X, Zhong S, Zhang M, Chen S, Shen Z
Received 11 August 2017
Accepted for publication 22 October 2017
Published 14 November 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 611—626
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S148856
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Kenan Onel
Background: We aimed to
evaluate the prognostic value of site-specific metastases in patients with
metastatic bladder cancer and analyze the roles that surgeries play in the
treatment of this malignancy.
Materials and methods: A population-based retrospective study using Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results dataset was performed and metastatic bladder cancer patients were classified according to the sites of metastases (bone, brain, liver, lung and distant lymph nodes). Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test was used for survival comparisons. Multivariate Cox regression model was employed to analyze the effect of distant metastatic sites on overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS).
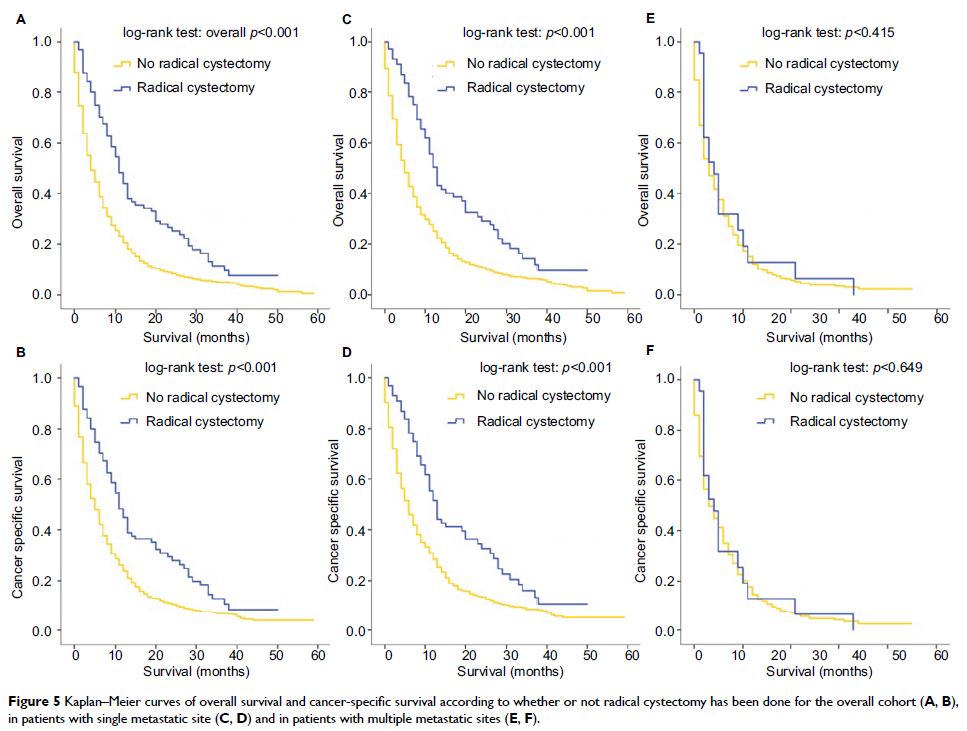
Results: A total of 1862 patients with metastatic bladder cancer from 2010 to 2014 were identified. Bone, lung and distant lymph nodes were the most common metastatic sites. Patients with bone, brain, liver and lung involvement had worse OS and CSS compared to patients without the corresponding sites of metastases. Multivariate analysis showed that bone, brain, liver and lung metastases were independent prognostic factors for both OS and CSS, while distant node metastasis was not. Moreover, patients with a single metastatic site had more favorable OS (p <0.001) and CSS (p <0.001) than patients with multisite metastases. Among single-site metastatic patients, distant nodes and liver metastases represented the best and the worst prognosis, respectively. Moreover, radical cystectomy was an independent predictor for better OS and CSS, while in patients with liver metastasis and multiple metastatic sites, RC did not bring benefits. Besides, in patients with a single metastatic site, metastasectomy seemed to be associated with favorable OS (p =0.042), especially for patients with age <65 years (p =0.006) and for muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients (p =0.031).
Conclusion: Distant metastatic sites have differential impact on survival outcomes in patients with metastatic bladder cancer. Surgeries, including radical cystectomy and metastasectomy, might still lead to survival benefits for highly selected patients.
Keywords: bladder cancer, metastatic site, prognosis, radical cystectomy, metastasectomy, Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results
Materials and methods: A population-based retrospective study using Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results dataset was performed and metastatic bladder cancer patients were classified according to the sites of metastases (bone, brain, liver, lung and distant lymph nodes). Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test was used for survival comparisons. Multivariate Cox regression model was employed to analyze the effect of distant metastatic sites on overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS).
Results: A total of 1862 patients with metastatic bladder cancer from 2010 to 2014 were identified. Bone, lung and distant lymph nodes were the most common metastatic sites. Patients with bone, brain, liver and lung involvement had worse OS and CSS compared to patients without the corresponding sites of metastases. Multivariate analysis showed that bone, brain, liver and lung metastases were independent prognostic factors for both OS and CSS, while distant node metastasis was not. Moreover, patients with a single metastatic site had more favorable OS (p <0.001) and CSS (p <0.001) than patients with multisite metastases. Among single-site metastatic patients, distant nodes and liver metastases represented the best and the worst prognosis, respectively. Moreover, radical cystectomy was an independent predictor for better OS and CSS, while in patients with liver metastasis and multiple metastatic sites, RC did not bring benefits. Besides, in patients with a single metastatic site, metastasectomy seemed to be associated with favorable OS (p =0.042), especially for patients with age <65 years (p =0.006) and for muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients (p =0.031).
Conclusion: Distant metastatic sites have differential impact on survival outcomes in patients with metastatic bladder cancer. Surgeries, including radical cystectomy and metastasectomy, might still lead to survival benefits for highly selected patients.
Keywords: bladder cancer, metastatic site, prognosis, radical cystectomy, metastasectomy, Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results