108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
CYP2D6 * 10 多态性对亚洲乳腺癌患者辅助性三苯氧胺治疗的影响:一项综合分析
Authors Lu J, Li H, Guo P, Shen R, Luo Y, Ge Q, Shi WF, Li Y, Zhu W
Received 15 August 2017
Accepted for publication 11 October 2017
Published 13 November 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5429—5437
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S149197
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Objective: To evaluate the
effect of CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism (C
100C>T, rs1065852) on clinical outcomes of female Asian breast cancer
patients with tamoxifen adjuvant treatment.
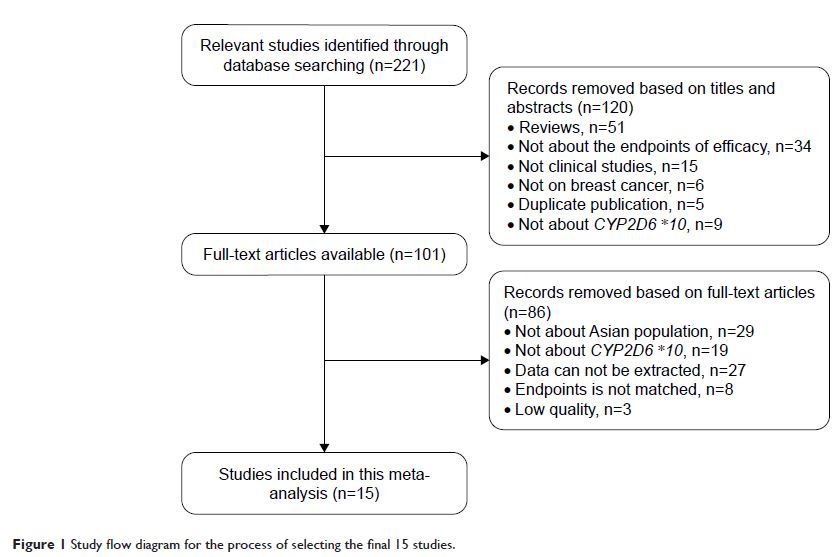
Methods: Meta-analysis of retrospective cohort studies published in July 2017 was performed. Fifteen studies with 1,794 Asian breast cancer patients were included, using strict eligibility requirements. Associations of disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS) and recurrence rate after tamoxifen intake, with CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism were investigated through random effects models.
Results: CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism was found to have effect on DFS and recurrence rate in various comparison models, but not on overall survival in the female Asian breast cancer patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our meta-analysis suggests that significant association of *10/*10 (TT ) genotype with poorer DFS and recurrence exists in female Asian breast cancer patients with tamoxifen 20 mg/day adjuvant treatment. In the future, large and well-designed studies are required to illustrate the interactions of CYP2D6 genetic variants, including *10 polymorphism and tamoxifen response on female breast cancer patients.
Keywords: CYP2D6 *10 , polymorphism, breast cancer, Asia, tamoxifen adjuvant treatment
Methods: Meta-analysis of retrospective cohort studies published in July 2017 was performed. Fifteen studies with 1,794 Asian breast cancer patients were included, using strict eligibility requirements. Associations of disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS) and recurrence rate after tamoxifen intake, with CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism were investigated through random effects models.
Results: CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism was found to have effect on DFS and recurrence rate in various comparison models, but not on overall survival in the female Asian breast cancer patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our meta-analysis suggests that significant association of *10/*10 (TT ) genotype with poorer DFS and recurrence exists in female Asian breast cancer patients with tamoxifen 20 mg/day adjuvant treatment. In the future, large and well-designed studies are required to illustrate the interactions of CYP2D6 genetic variants, including *10 polymorphism and tamoxifen response on female breast cancer patients.
Keywords: CYP2D6 *10 , polymorphism, breast cancer, Asia, tamoxifen adjuvant treatment