108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

GEMIN4 基因多态性与癌症发病风险:一项综合分析
Authors Wu N, Zhang X, Tian J, Yu S, Qiao Y
Received 25 July 2017
Accepted for publication 29 September 2017
Published 2 November 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5263—5271
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S147204
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Abstract: Gem-associated protein 4 (GEMIN4 ) gene is a key regulator
for the miRNA biogenesis processes. Recent studies have demonstrated that some
single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in GEMIN4 gene
are associated with the risk of cancer, but the results are still
controversial. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis to analyze the
association between three major SNPs (rs2740348, rs7813, and rs3744741) in
the GEMIN4 gene and the risk of
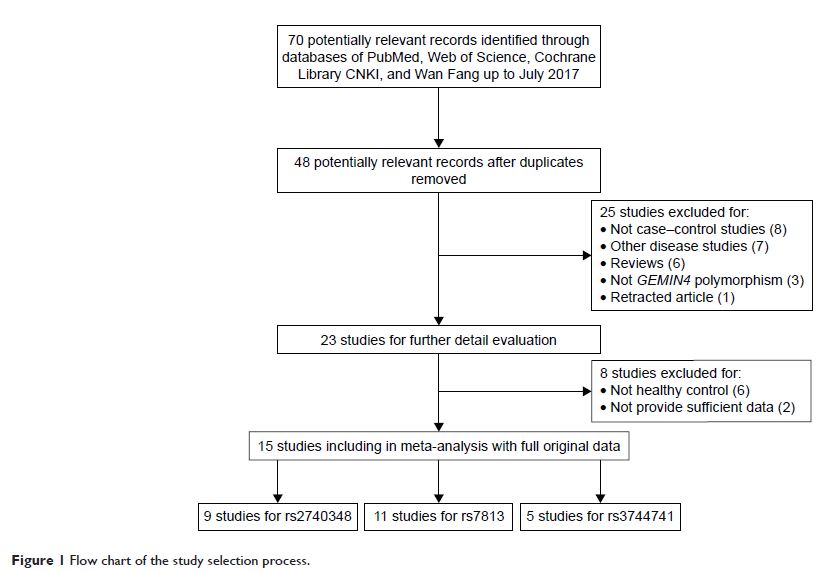
cancer. Relevant articles were searched in Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane
Library, Chinese Wan Fang, and Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure
databases. Pooled odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was
calculated to quantitatively estimate the association. Publication bias and
sensitivity analyses were undertaken to evaluate the stability of the results.
Overall, the pooled results showed that rs2740348 involving 3,604 cases and
3,770 controls was significantly associated with increased cancer risk (GG vs
GC/CC: OR =1.16, 95% CI =1.05–1.29, P =0.004) and rs7813
involving 4,729 cases and 4,562 controls was also related to increased cancer
risk (TT vs TC/CC: OR =1.12, 95% CI =1.03–1.22, P =0.009). However, there was no
significant association between rs3744741 and cancer risk under overall genetic
models. In conclusion, our study has demonstrated that rs2740348 and rs7813 are
associated with increased risk of cancer, and they may be new biomarkers for
predicting cancer risk.
Keywords: gem-associated
protein 4, single-nucleotide polymorphism, cancer, meta-analysis