108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

氧化锌纳米粒子在人神经母细胞瘤 SHSY5Y 细胞中以尺寸依赖的方式诱导毒性反应
Authors Liu J, Kang Y, Yin S, Song B, Wei L, Chen L, Shao L
Received 14 August 2017
Accepted for publication 27 September 2017
Published 1 November 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 8085—8099
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S149070
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
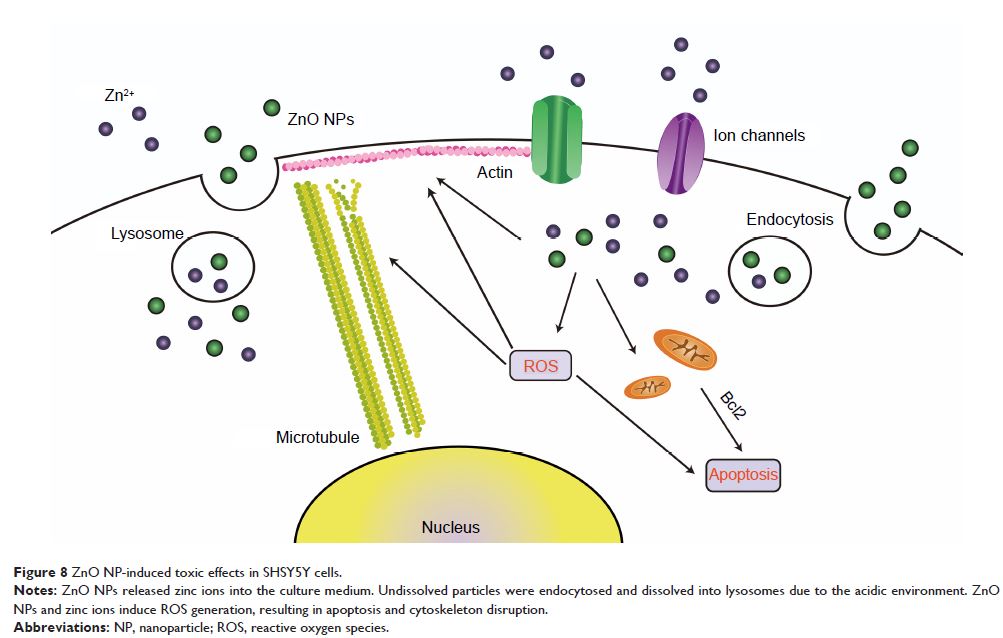
Abstract: Due to the widespread applications of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO
NPs), the potential exposure of workers, consumers, and scientists to these
particles has increased. This potential for exposure has attracted extensive
attention in the science community. Many studies have examined the
toxicological profile of ZnO NPs in the immune system, digestive system,
however, information regarding the toxicity of ZnO NPs in the nervous system is
scarce. In this study, we detected the cytotoxicity of two types of ZnO NPs of
various sizes – ZnOa NPs and ZnOb NPs – and we characterized the shedding
ability of zinc ions within culture medium and the cytoplasm. We found that reactive oxygen species played a crucial role in ZnO
NP-induced cytotoxicity, likely because zinc ions were leached from ZnO NPs.
Apoptosis and cytoskeleton changes were also toxic responses induced by the ZnO
NPs, and ZnOb NPs induced more significant toxic responses
than ZnOa NPs in SHSY5Y cells. In conclusion, ZnO NPs
induced toxic responses in SHSY5Y cells in a size-dependent manner, which can
probably be attributed to their ion-shedding ability.
Keywords: zinc
oxide, nanoparticles, SHSY5Y cells, reactive oxygen species, apoptosis, cell
cytoskeleton