108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对 AQP4-IgG 视神经脊髓炎-视神经炎患者和 MOG-IgG 视神经炎患者的区域同质化的自发性脑活动进行比较:静息态功能性磁共振成像研究
Authors Wang J, Tian Y, Shao Y, Feng H, Qin L, Xu W, Liu H, Xu Q, Wei S, Ma L
Received 29 June 2017
Accepted for publication 15 August 2017
Published 24 October 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 2669—2679
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S145183
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Roger Pinder
Objective: Many previous studies have demonstrated that neuromyelitis optica
(NMO) patients have abnormalities of brain anatomy and function. However,
differences in spontaneous brain activity between myelin oligodendrocyte
glycoprotein (MOG)-IgG ON and aquaporin 4(AQP4)-neuromyelitis optica-optic
neuritis (ON) remain unknown. In the current study, we investigated the brain
neural homogeneity in MOG-IgG ON versus AQP4-IgG NMO-ON subjects by regional
homogeneity (ReHo) method using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Patients and methods: A total of 32 NMO-ON and ON subjects (21 with
AQP4-IgG+NMO-ON and 11 with MOG-IgG+ON) and 34 healthy controls (HCs) closely
matched for age were recruited, and scans were performed for all subjects. A
one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to determine the regions in
which the ReHo was different across the three groups. NMO-ON and ON subjects
were distinguished from HCs by a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
The relationship between the mean ReHo in many brain regions and clinical
features in NMO subjects was calculated by Pearson correlation analysis.
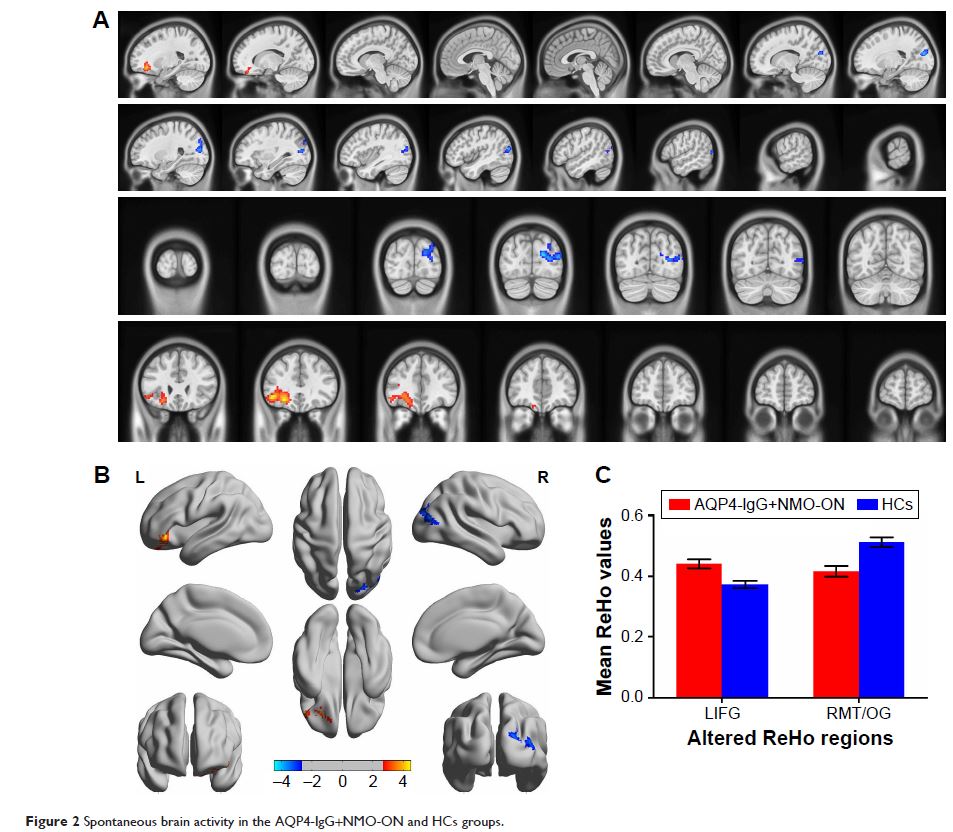
Results: Compared with HCs, MOG-IgG+ON subjects had
significantly decreased ReHo values in the posterior lobe of the left
cerebellum and increased ReHo values in the left inferior frontal gyrus, right
prefrontal gyrus, and left precentral/postcentral gyrus. AQP4-IgG+NMO-ON
subjects showed higher ReHo values in the left inferior frontal gyrus and right
middle temporal/occipital gyrus. Compared with MOG-IgG+ON subjects,
AQP4-IgG+NMO-ON subjects had lower ReHo values in the posterior lobe of the
right cerebellum. AQP4-Ig+NMO-ON subjects showed higher ReHo values in the left
precentral/postcentral gyrus and right superior temporal gyrus.
Conclusion: AQP4-IgG+NMO-ON and MOG-IgG+ON subjects showed
abnormal synchronized neuronal activity in many brain regions, which is
consistent with deficits in visual, motor, and cognitive function. Furthermore,
different patterns of synchronized neuronal activity occurred in the AQP4-IgG+NMO-ON
and MOG-IgG+ON.
Keywords: neuromyelitis
optica-optic neuritis, MOG-IgG, AQP4-IgG, regional homogeneity, resting state,
functional magnetic resonance imaging