108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

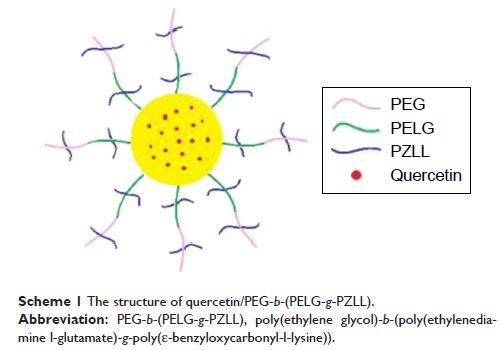
槲皮素 (Quercetin) 纳米颗粒复合物通过调节内皮细胞 ICAM-1 的表达水平来减缓糖尿病肾病
Authors Tong F, Liu S, Yan B, Li X, Ruan S, Yang S
Received 21 July 2017
Accepted for publication 25 September 2017
Published 24 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 7799—7813
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S146978
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: The purpose of the study was to reveal the therapeutic effect of
quercetin (QUE) nanoparticle complex on diabetic nephropathy (DN) by regulating
the expression of intercellular adhesion molecular-1 (ICAM-1) on endothelium as
compared to free QUE. QUE 10 mg/kg as a single abdominal subcutaneous injection
daily for 8 weeks continuously in diabetic rats and 10 mg/kg QUE nanoparticle
complex as a single abdominal subcutaneous injection every 5 days, continuously
administered for 8 weeks to diabetic rats. Blood and left kidneys were
collected; pathological change of kidney, renal function, oxidative stress
level, blood glucose level, serum lipid, urine protein, and albumin/creatinine
ratio were measured; and neutrophil adhesion, ICAM-1 expression, and CD11b+ cells infiltration were observed. Both QUE and QUE
nanoparticle complex preconditioning ameliorated the pathological damage of
kidney and improved renal function, alleviated renal oxidative stress injury,
restricted inflammatory cells infiltration, and downregulated the ICAM-1
expression as compared to DN group, while QUE nanoparticle complex
significantly alleviated this effect.
Keywords: nanoparticle
complex, quercetin, DN, ICAM-1, CD11b+, endothelium