108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA 和 RNAi 介导的 SIRT7 敲除后 MDA-MB-231 细胞中的 mRNA 谱
Authors Chen KL, Li L, Wang YR, Li CM, Badri TM, Wang GL
Received 13 August 2017
Accepted for publication 26 September 2017
Published 24 October 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 5115—5128
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S149048
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Abstract: Breast
cancer is one of the most common malignant cancers among women and a major
clinical obstacle. Although studies have reported the abnormal expression of
SIRT7 in breast cancer, whether the function of SIRT7 regulates the expression
of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in breast cancer remains unknown. We aimed to
determine the differential expressions of mRNAs and lncRNAs associated with
SIRT7 and understand the regulatory mechanism of SIRT7 in breast cancer. RNA
sequencing was performed to explore the transcriptome in MDA-MB-231 cells after
SIRT7 depletion, and a total of 50,634 different transcripts were identified.
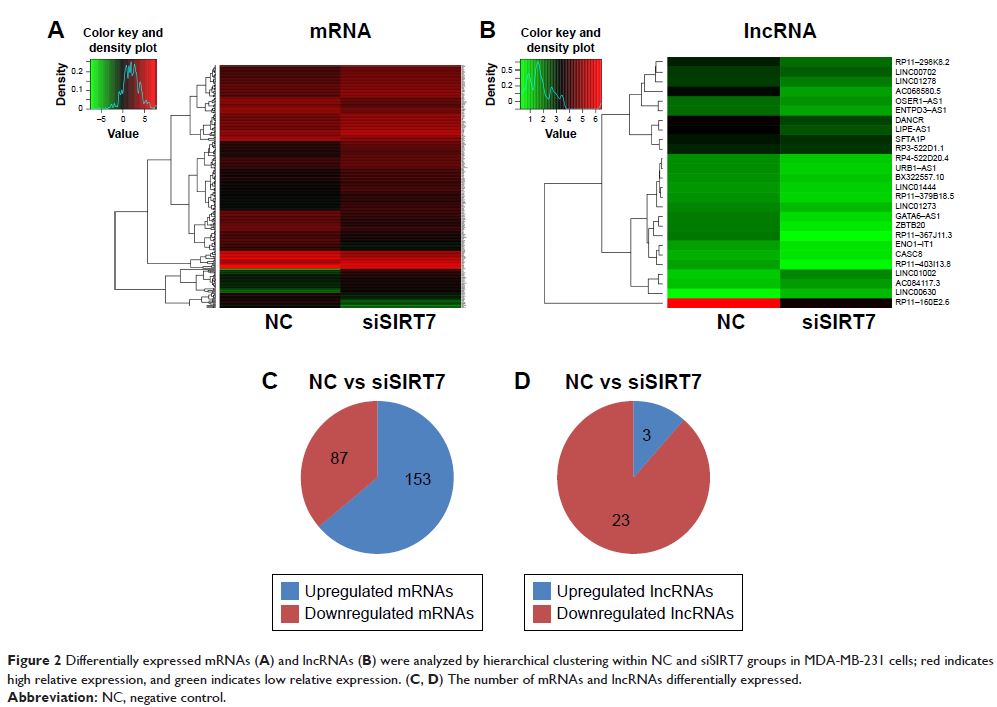
In comparison with the negative control, siSIRT7 groups showed 240
differentially expressed mRNAs and 26 differentially expressed lncRNAs. Gene ontology
analysis revealed that the differentially expressed mRNAs mainly regulated DNA
replication, CXCR chemokine receptor binding, and maturation of large subunit
rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript, nucleoplasm, mitochondrion, and NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and
Genomes analysis showed that the differentially expressed mRNAs were mainly
involved in pathways associated with MAPK signaling pathway, tumor necrosis
factor signaling pathway, hepatitis B, and cancer. Moreover, the target genes
of the differentially expressed lncRNAs mainly regulated the carboxylic acid
metabolic processes and were involved in glycolysis pathway. The mRNA-lncRNA
coexpression network comprised 186 mRNAs and 23 lncRNAs. Our results provide essential
data regarding differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs after the depletion
of SIRT7 in breast cancer cells, which may be useful to elucidate the role of
SIRT7 in breast cancer development.
Keywords: SIRT7, breast cancer cell, lncRNA, mRNA, RNA-Seq