108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Development and utilization of the Medicines Use Review patient satisfaction questionnaire
Authors Hindi A, Parkhurst C, Rashidi Y, Ho SY, Patel N, Donyai P
Received 21 July 2017
Accepted for publication 14 September 2017
Published 20 October 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1797—1806
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S146991
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Doris Leung
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Johnny Chen
Abstract: The Medicines Use Review is a community pharmacy service funded in the
United Kingdom to improve patients’ adherence to medication and reduce
medicines waste. The objective was to develop, pilot, and utilize a new
Medicines Use Review patient satisfaction questionnaire. A questionnaire for
patient self-completion was developed using a published framework of patient
satisfaction with the Medicines Use Review service. The questions were
validated using the content validity index and the questionnaire piloted through
three pharmacies (February–April 2016). The revised questionnaire contained 12
questions with responses on a 5-point Likert scale, and a comments box. The
questionnaire was distributed to patients following a Medicines Use Review
consultation via community pharmacies (June–October 2016). Exploratory factor
analysis and Cronbach’s α were performed to investigate the relationships
between the items and to examine structural validity. The survey results were
examined for patients’ reported satisfaction with Medicines Use Reviews, while
the handwritten comments were thematically analyzed and mapped against the
questionnaire items. An estimated 2,151 questionnaires were handed out, and a
total of 505 responses were received indicating a 24% response rate.
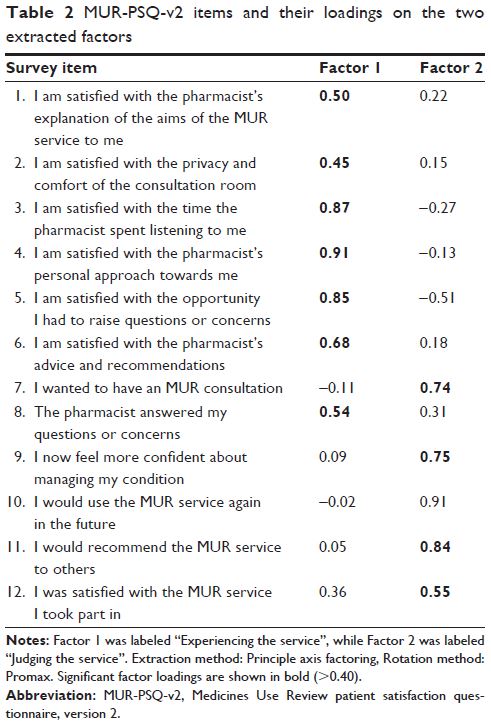
Exploratory factor analysis revealed two factors with a cumulative variance of
68.8%, and Cronbach’s α showed high internal consistency for each factor
(α=0.90 and α=0.89, respectively). The survey results demonstrated that
patients could show a high degree of overall satisfaction with the service,
even if initially reluctant to take part in a Medicines Use Review. The results
support the Medicines Use Review patient satisfaction questionnaire as a
suitable tool for measuring patient satisfaction with the Medicines Use Review
service. A wider study is needed to confirm the findings about this community
pharmacy-based adherence service.
Keywords: community
pharmacy, Medicines Use Review, patient satisfaction, questionnaire, adherence