108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

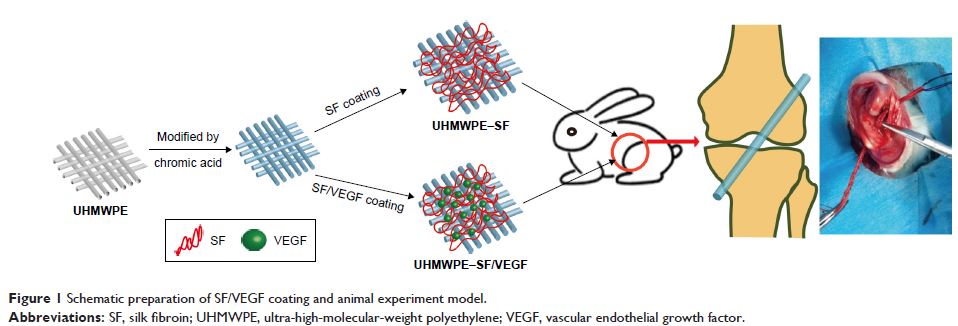
表面改性并含有血管内皮生长因子的丝素蛋白可通过促进血管生成来改善超高分子量聚乙烯的生物学性能
Authors Ai C, Sheng D, Chen J, Cai J, Wang S, Jiang J, Chen S
Received 10 August 2017
Accepted for publication 17 September 2017
Published 20 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 7737—7750
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S148845
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) has been applied in
orthopedics, as the materials of joint prosthesis, artificial ligaments, and
sutures due to its advantages such as high tensile strength, good wear
resistance, and chemical stability. However, postoperative osteolysis induced
by UHMWPE wear particles and poor bone–implant healing interface due to
scarcity of osseointegration is a significant problem and should be solved
imperatively. In order to enhance its affinity to bone tissue, vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was loaded on the surface of materials, the
loading was performed by silk fibroin (SF) coating to achieve a
controlled-release delivery. Several techniques including field emission
scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and attenuated total reflectance
(ATR)-Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and water contact angle measurement
were used to validate the effectiveness of introduction of SF/VEGF. The result
of ELISA demonstrated that the release of VEGF was well maintained up to
4 weeks. The modified UHMWPE was evaluated by both in vitro and in vivo
experiments. According to the results of FESEM and cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8)
assay, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cultured on the UHMWPE coated with
SF/VEGF and SF exhibited a better proliferation performance than that of the
pristine UHMWPE. The model rabbit of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
was used to observe the graft–bone healing process in vivo. The results of
histological evaluation, microcomputed tomography (micro-CT) analysis, and
biomechanical tests performed at 6 and 12 weeks after surgery demonstrated
that graft–bone healing could be significantly improved due to the effect of
VEGF on angiogenesis, which was loaded on the surface by SF coating. This study
showed that the method loading VEGF on UHMWPE by SF coating played an effective
role on the biological performance of UHMWPE and displayed a great potential
application for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.
Keywords: UHMWPE, surface modification, VEGF, silk fibroin, graft–bone healing