108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

超临界二氧化碳法制备的丝素蛋白纳米平台用于智能结肠癌治疗
Authors Xie MB, Fan DJ, Li Y, He XW, Chen XM, Chen YF, Zhu JX, Xu GB, Wu XJ, Lan P
Received 28 June 2017
Accepted for publication 29 August 2017
Published 20 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 7751—7761
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S145012
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Dongwoo Khang
Purpose: To deliver insoluble natural compounds into colon cancer cells in a
controlled fashion.
Materials and methods: Curcumin (CM)–silk fibroin (SF) nanoparticles
(NPs) were prepared by solution-enhanced dispersion by supercritical CO2 (SEDS) (20 MPa pressure, 1:2 CM:SF ratio, 1%
concentration), and their physicochemical properties, intracellular uptake
efficiency, in vitro anticancer effect, toxicity, and mechanisms were evaluated
and analyzed.
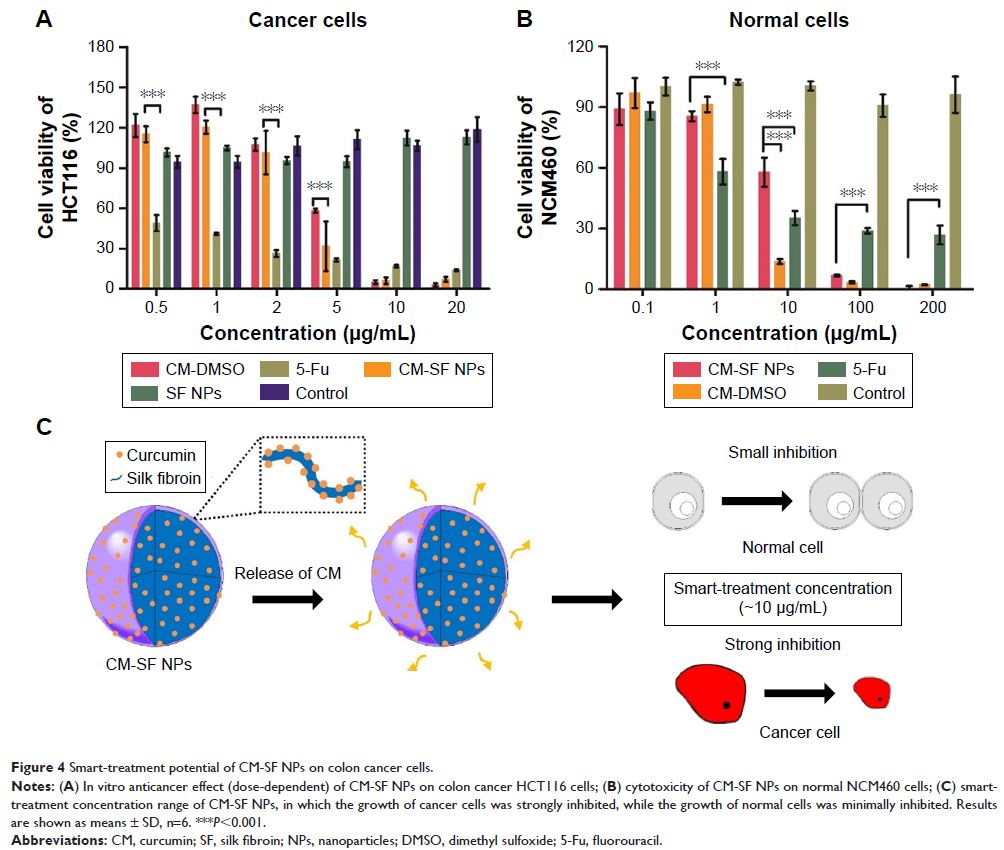
Results: CM-SF NPs (<100 nm) with controllable particle size
were prepared by SEDS. CM-SF NPs had a time-dependent intracellular uptake
ability, which led to an improved inhibition effect on colon cancer cells.
Interestingly, the anticancer effect of CM-SF NPs was improved, while the side
effect on normal human colon mucosal epithelial cells was reduced by a
concentration of ~10 µg/mL. The anticancer mechanism involves cell-cycle arrest
in the G0/G1 and G2/M phases in association with inducing apoptotic
cells.
Conclusion: The natural compound-loaded SF nanoplatform prepared
by SEDS indicates promising colon cancer-therapy potential.
Keywords: supercritical,
silk fibroin, nanoparticle, natural compounds, colon cancer