108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

加载甲氨蝶呤 (Methotrexate) 的植入物对 S180 荷瘤小鼠有增强的抗肿瘤功效
Authors Gao L, Xia L, Zhang R, Duan D, Liu X, Xu J, Luo L
Received 14 June 2017
Accepted for publication 11 September 2017
Published 20 October 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 3065—3075
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S143942
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Rammohan Devulapally
Peer reviewer comments 5
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Purpose: Methotrexate is widely used in chemotherapy for a variety of malignancies.
However, severe toxicity, poor pharmacokinetics, and narrow safety margin of
methotrexate limit its clinical application. The aim of this study was to
develop sustained-release methotrexate-loaded implants and evaluate antitumor
activity of the implants after intratumoral implantation.
Materials and methods: We prepared the implants containing
methotrexate, poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), and polyethylene glycol 4000 with
the melt-molding technique. The implants were characterized with regards to
drug content, morphology, in vitro, and in vivo release profiles. Differential
scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
were carried out to investigate the physicochemical properties of the implants.
Furthermore, the antitumor activity of the implants was tested in a sarcoma 180
mouse model.
Results: The implants were prepared as solid rods.
Scanning electron microscopy images showed a smooth surface of the implant,
suggesting that methotrexate was homogeneously dispersed in the polymeric
matrix. The results of DSC and FTIR indicated that no significant interaction
between methotrexate and the polymer was observed in the implants. Both in
vitro and in vivo release profiles of the implants were characterized by burst
release followed by sustained release of methotrexate. Intratumoral
implantation of methotrexate-loaded implants could efficiently delay tumor
growth. Moreover, an increase in the dose of implants led to a higher tumor
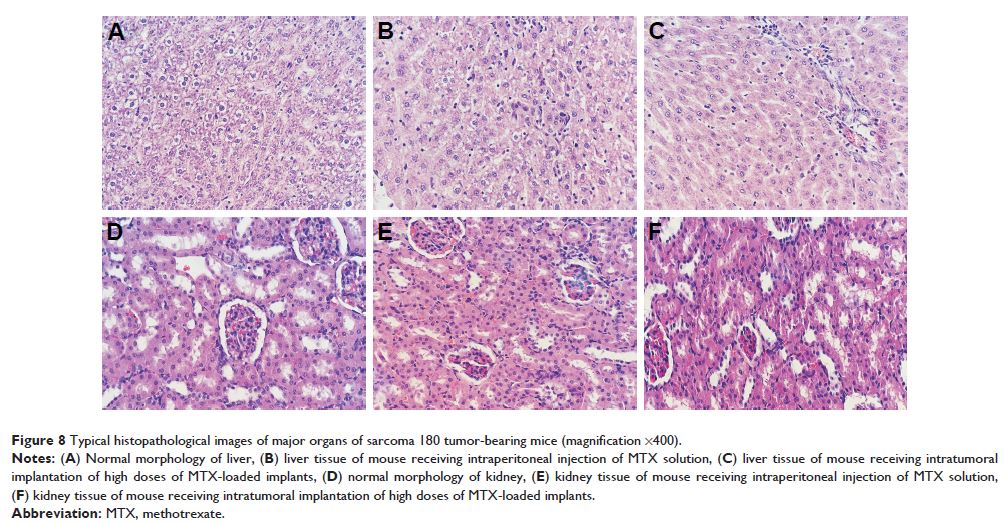
suppression rate without additional systemic toxicity.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that
methotrexate-loaded implants had significant antitumor efficacy in a sarcoma
180 mouse model without dose-limiting side effects, and suggest that the
implants could be potentially applied as an intratumoral delivery system to
treat cancer.
Keywords: methotrexate,
implant, sustained release, poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), intratumoral
chemotherapy
摘要视频链接:Enhanced antitumor efficacy
of MTX-loaded implants