108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

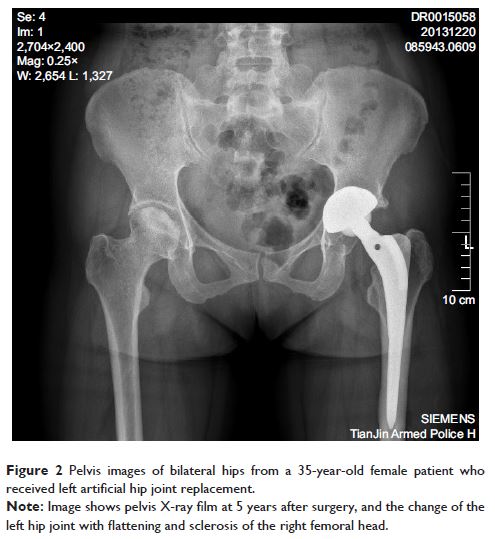
对股骨头坏死的严重急性呼吸系统综合征患者综合治疗的 12 年随访研究
Authors Liu T, Ma J, Su B, Wang H, Wang Q, Ma X
Received 28 April 2017
Accepted for publication 11 September 2017
Published 19 October 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1449—1454
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S140694
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Objective: To investigate the long-term efficacy of a combination treatment
of alendronate, extracorporeal shock and hyperbaric oxygen for osteonecrosis of
the femoral head (ONFH) of post-severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
patients.
Patients and methods: The retrospective study was performed including a
total of 37 post-SARS ONFH patients (66 hip joints) in the Department of
Orthopedics of the General Hospital of Tianjin Medical University between
November 2003 and November 2015, consisting of 6 males (11 hip joints) and 31
females (55 hip joints), with age between 19 and 47 years (average
29.9 years). Visual analog scale (VAS) score, Harris score and Association
Research Circulation Osseous (ARCO) stage of imaging examination were compared
among those before treatment, and at 1, 3, 6, 9 and 12 years after
treatment. Paired t-test was used for
statistical analysis of VAS and Harris score before and after treatment.
Difference of effective rate on all stages was analyzed with Chi-square test.
Results: With 12-year follow-up, significant improvements
on VAS (6.81 of pre-treatment vs 3.94 of 12-year post-treatment) and Harris
score (74.54 of pre-treatment vs 80.14 of 12-year post-treatment) were observed
(all p <0.05). Effective rate showed
statistical significance among three stages of ARCO (p <0.05). The combined treatment
showed different efficacies on different ARCO stages; the best was on ARCO
Phase I.
Conclusion: The combined treatment may delay or discontinue the
development of ONFH in post-SARS patients.
Keywords: SARS,
osteonecrosis of the femoral head, alendronate, extracorporeal shock wave,
hyperbaric oxygen