108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

鉴定患有常染色体隐性进行性肌阵挛性癫痫的一个中国家族的新型 CACNA1A 基因突变
Authors Lv YD, Wang Z, Liu C, Cui L
Received 7 July 2017
Accepted for publication 21 August 2017
Published 19 October 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 2631—2636
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S145774
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Roger Pinder
Background: Progressive myoclonic epilepsy (PME) is a heterogeneous
neurodegenerative disorder, which is commonly manifested with refractory
seizures and neurologic deterioration. The prognosis of PME is poor, so early
diagnosis of PME is critical. The aim of our study is to identify the novel
pathogenic gene in a Chinese family with PME, which may be helpful in future.
Subjects and methods: A three-generation consanguineous Chinese Han
family with PME was recruited. A novel homozygous variant was identified by the
genetic technique of exome sequencing and certificated by Sanger sequencing and
functional prediction.
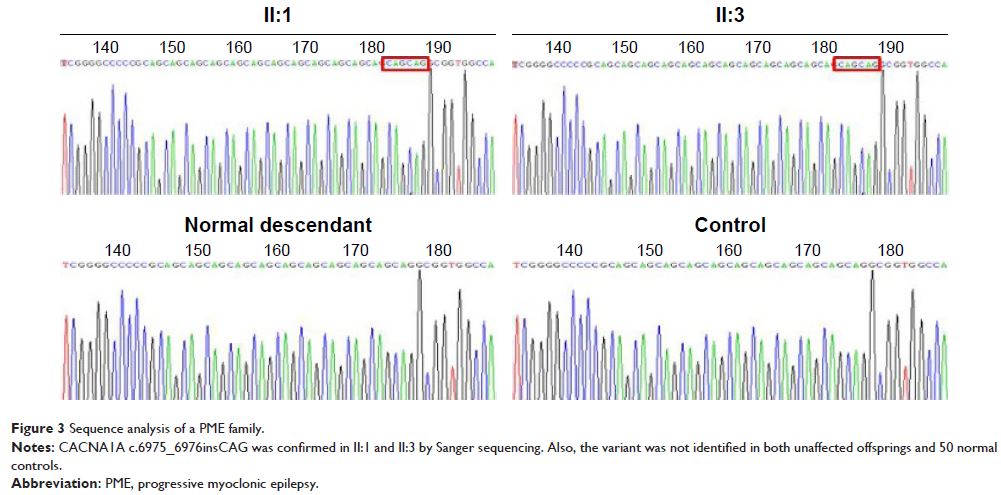
Results: A
novel homozygous variant, c.6975_6976insCAG, in the CACNA1A was identified in
the PME family. The novel variant encoding the alpha-1A subunit of the calcium
channel Cav2.1 was found in two siblings in the Chinese family and was absent
in 50 normal controls. Our research indicates that the homozygous c.6975_6976insCAG
might be the pathogenic mutation for PME.
Conclusion: As a molecular diagnostic strategy, our research
explores the mutation gene spectrum of PME and has resulted in significant
predictions for genetic counseling.
Keywords: CACNA1A, PME,
exome sequencing, myoclonus, muscular hypotonia