108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

鉴定与早期老年黄斑变性的生物调节有关的 lncRNA
Authors Zhu W, Meng YF, Xing Q, Tao JJ, Lu J, Wu Y
Received 23 April 2017
Accepted for publication 26 June 2017
Published 17 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 7589—7602
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S140275
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Age-related
macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the most common causes of adult blindness
in developed countries. However, the role of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in
the development and progression of early AMD is unclear.
Methods: We established the lncRNA profile of early AMD by reannotation of
microarrays from the gene expression omnibus database. Quantitative real-time
polymerase chain reaction was used to determine the expression of selected
lncRNAs.
Results: The expression profiles of 9 cases of AMD and 7 controls were studied. A
total of 266 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected (94
upregulated and 172 downregulated). Among all the DEGs, 64 were lncRNAs.
Advanced bioinformatics analyses demonstrated that differentially expressed
lncRNAs could play significant roles in visual perception, sensory perception
of light stimulus, and cognition. The pathway analyses showed that the two most
significantly influenced Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways were
those of phototransduction and purine metabolism. By the analyses of the key
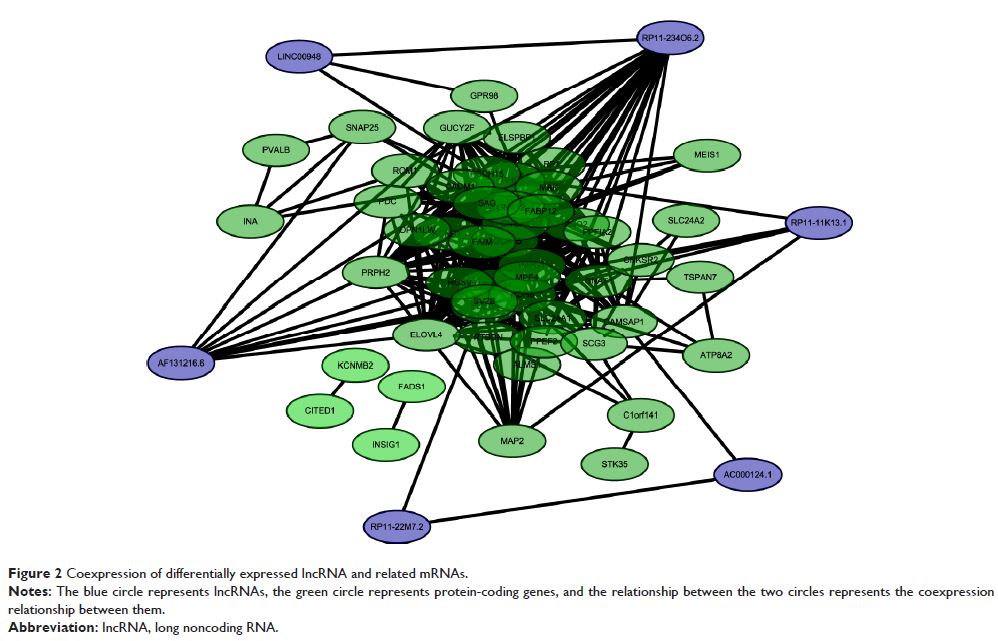
lncRNAs, it was found that RP11-234O6.2 was downregulated in the aging retinal
pigment epithelium (RPE) cellular model. Exogenous RP11-234O6.2 treatment led
to increased cell viability and improved apoptosis but it did not affect the
cell migration ability of aging RPE cells.
Conclusion: This study indicated that lncRNAs are differentially expressed in
early AMD and may produce important regulative effects. An lncRNA,
RP11-234O6.2, might be involved in the biological regulation of early AMD and
have therapeutic potential.
Keywords: age-related macular degeneration, lncRNAs, microarray, bioinformatics
analyses