108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

靶向骨吸收表面的纳米颗粒用于递送抗 miR214 以进行骨质疏松治疗
Authors Cai M, Yang L, Zhang S, Liu J, Sun Y, Wang X
Received 16 April 2017
Accepted for publication 25 July 2017
Published 13 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 7469—7482
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S139775
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
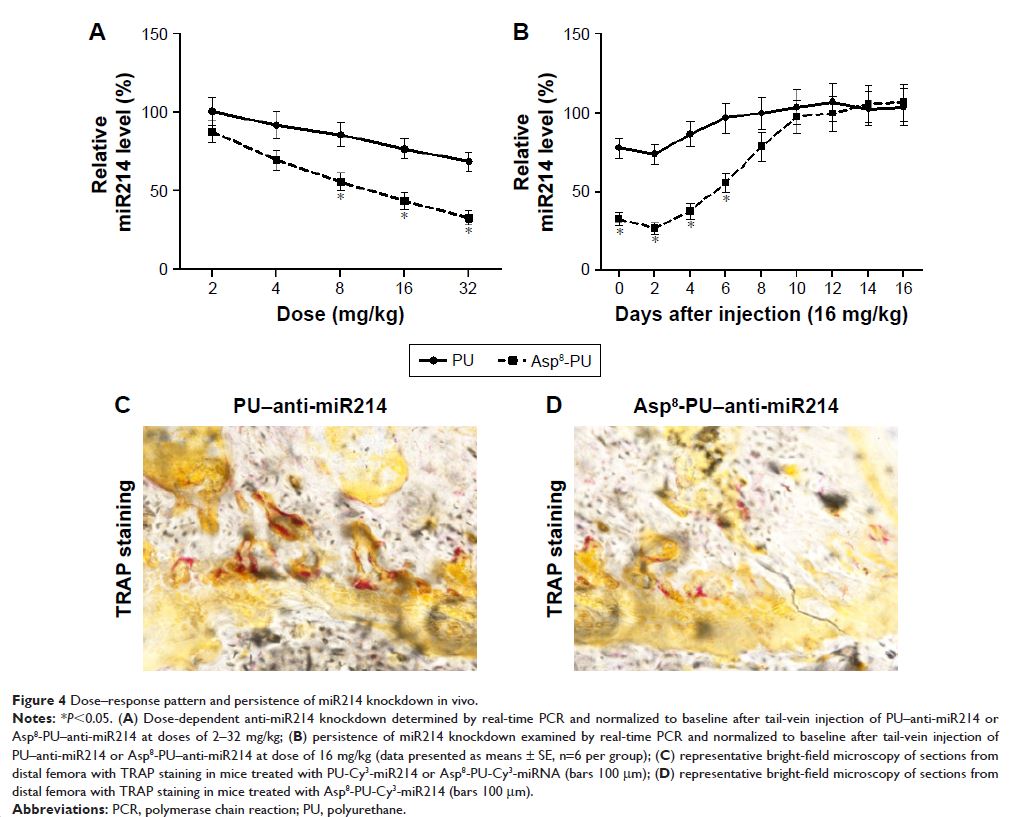
Abstract: With increasing fracture risks due to fragility, osteoporosis is a
global health problem threatening postmenopausal women. In these patients,
osteoclasts play leading roles in bone loss and fracture. How to inhibit
osteoclast activity is the key issue for osteoporosis treatment. In recent
years, miRNA-based gene therapy through gene regulation has been considered a
potential therapeutic method. However, in light of the side effects, the use of
therapeutic miRNAs in osteoporosis treatment is still limited by the lack of
tissue/cell-specific delivery systems. Here, we developed polyurethane (PU)
nanomicelles modified by the acidic peptide Asp8. Our data showed
that without overt toxicity or eliciting an immune response, this delivery
system encapsulated and selectively deliver miRNAs to OSCAR+ osteoclasts at bone-resorption surface in
vivo. With the Asp8-PU delivery system, anti-miR214
was delivered to osteoclasts, and bone microarchitecture and bone mass were
improved in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice. Therefore, Asp8-PU could be a useful bone-resorption
surface-targeting delivery system for treatment of osteoclast-induced bone diseases
and aging-related osteoporosis.
Keywords: osteoporosis,
microRNA, bone resorption, targeting delivery, nanoparticle