108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用 NF-κB 诱饵寡聚脱氧核苷酸修饰的抗原负载的树突状细胞来改善胶原诱导的关节炎
Authors Jiang HM, Hu HG, Zhang YL, Yue P, Ning LC, Zhou Y, Shi P, Yuan R
Received 3 July 2017
Accepted for publication 7 September 2017
Published 13 October 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 2997—3007
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S145421
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Abstract: Dendritic
cells (DCs) play an important role in the initiation of autoimmunity in
rheumatoid arthritis (RA); therefore, the use of DCs needs to be explored to develop
new therapeutic approaches for RA. Here, we investigated the therapeutic effect
of bovine type II collagen (BIIC)-loaded DCs modified with NF-κB decoy
oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) on collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in rats and
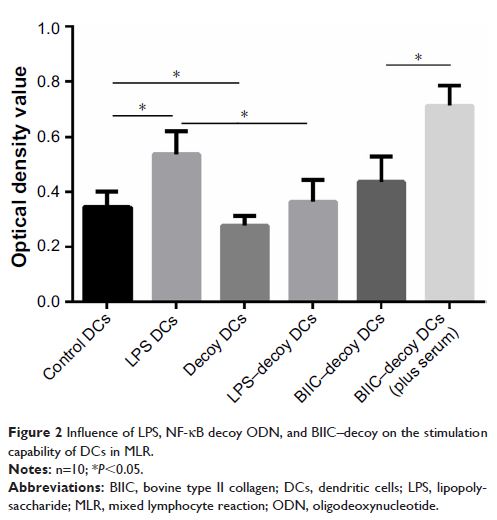
explored the underlying mechanisms. DCs treated with BIIC and NF-κB decoy ODNs
exhibited features of immature DCs with low levels of costimulatory molecule
(CD80 and CD86) expression. The development of arthritis in rats with CIA
injected with BIIC + NF-κB decoy ODN-propagated DCs (BIIC–decoy DCs) was
significantly ameliorated compared to that in rats injected with
BIIC-propagated DCs or phosphate-buffered saline. We also found that the
BIIC–decoy DCs exerted antiarthritis effects by inhibiting self-lymphocyte
proliferative response and suppressing IFN-γ and anti-BIIC antibody production
and inducing IL-10 antibody production. Additionally, antihuman serum
antibodies were successfully produced in the rats treated with BIIC–decoy DCs
but not in those treated with NF-κB decoy ODN-propagated DCs; moreover, the
BIIC–decoy DCs did not affect immune function in the normal rats. These
findings suggested that NF-κB decoy ODN-modified DCs loaded with a specific
antigen might offer a practical method for the treatment of human RA.
Keywords: NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides, collagen-induced arthritis,
dendritic cells, rheumatoid arthritis