108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

褪黑激素能够增强 “由内向外” 纳米热疗法对人乳腺癌细胞的作用:利用加载褪黑素的纳米复合物颗粒的潜在的癌症靶向多模态治疗
Authors Xie WS, Gao Q, Wang D, Wang W, Yuan J, Guo Z, Yan H, Wang X, Sun X, Zhao L
Received 7 August 2017
Accepted for publication 31 August 2017
Published 11 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 7351—7363
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S148520
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alicia Fernandez-Fernandez
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Dongwoo Khang
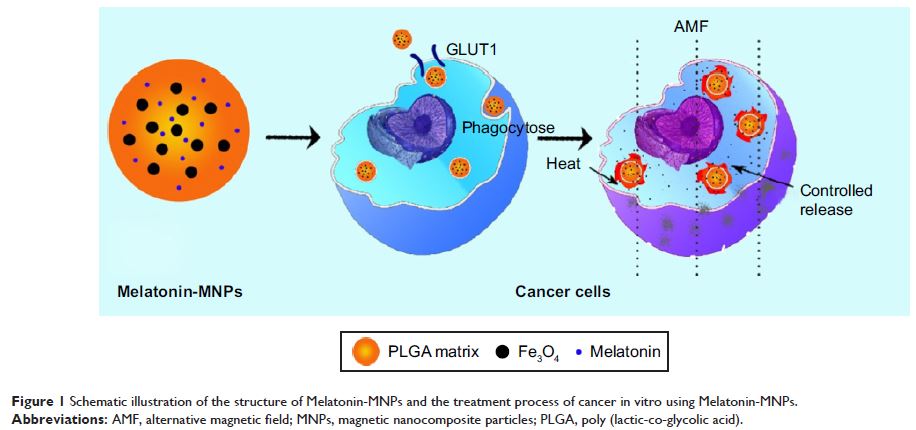
Purpose: With the wide recognition of oncostatic effect of melatonin, the current
study proposes a potential breast cancer target multimodality treatment based
on melatonin-loaded magnetic nanocomposite particles (Melatonin-MNPs).
Methods: Melatonin-MNPs were fabricated by the single
emulsion solvent extraction/evaporation method.
Results: Based on the facilitated transport of melatonin
by the GLUT overexpressed on the cell membrane, such Melatonin-MNPs can be more
favorably uptaken by MCF-7 cells compared with the melatonin-free nanocomposite
particles, which indicates the cancer targeting ability of melatonin molecule.
Inductive heating can be generated by exposure to the Melatonin-MNPs
internalized within cancer cells under alternative magnetic field, so as to
achieve the “inside-out” magnetic nano-thermotherapy. In addition to
demonstrating the superior cytotoxic effect of such nano-thermotherapy over the
conventional exogenous heating by metal bath, more importantly, the sustainable
release of melatonin from the Melatonin-MNPs can be greatly promoted upon
responsive to the magnetic heating. The multimodality treatment based on
Melatonin-MNPs can lead to more significant decrease in cell viability than any
single treatment, suggesting the potentiated effect of melatonin on the
cytotoxic response to nano-thermotherapy.
Conclusion: This study is the first to fabricate the
precisely engineered melatonin-loaded multifunctional nanocomposite particles
and demonstrate the potential in breast cancer target multimodality treatment.
Keywords: melatonin,
magnetic nano-thermotherapy, multifunctional nanoparticles, breast cancer,
cancer multimodality treatment, cancer target