108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国北方老年男性维生素 D 受体基因多态性与糖尿病血脂异常的关系
Authors Xia Z, Hu YZ, Han ZT, Gao Y, Bai J, He Y, Zhao H, Zhang H
Received 6 July 2017
Accepted for publication 6 September 2017
Published 10 October 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 1673—1679
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S145700
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Zhi-Ying Wu
Background: The prevalence of dyslipidemia is rising alarmingly in elderly Han
Chinese male patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The genetic factors
that contribute to the development of diabetic dyslipidemia remain incompletely
identified. This study was conducted to assess the association between vitamin
D receptor (VDR) polymorphisms and development of dyslipidemia in the Han
elderly male population with T2DM in North China.
Methods: A total of 242 T2DM patients with dyslipidemia
(DH group, n=108) or without dyslipidemia (DO group, n=134) and 100 controls
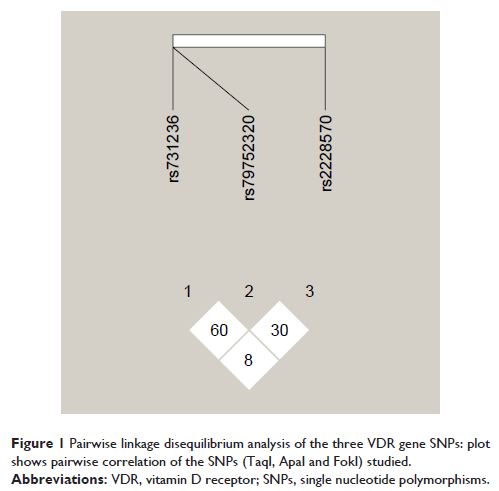
were genotyped for ApaI, TaqI and FokI single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
of the VDR gene using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length
polymorphism and sequencing. The frequency and distribution of the SNPs were
compared between cases and controls.
Results: The distribution of genotypes of VDR-FokI was
significantly different between the control and DM group (P =0.033), as well as between the
control and DH subgroup (P =0.011) but not DO
subgroup (P =0.111). The frequency of C
allele and CC genotype of FokI was significantly higher in the DH patients than
in the controls (P =0.015 and P =0.003, respectively).
Logistic regression analysis in a dominant model homozygous for the C allele of
the FokI SNP showed that CC genotype was associated with DH patients (OR
=1.797, 95% CI: 1.077–2.999, P =0.025). Significant
associations of the ApaI and TaqI SNPs with either DO or DH subjects were not
observed.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that CC genotype of VDR-FokI is
a risk factor for T2DM patients with dyslipidemia in elderly males in North
China.
Keywords: vitamin
D receptor, VDR, diabetes, dyslipidemia, polymorphism, elderly