108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

常山酮 (Halofuginone) 通过 AMPK 激活缓解严重急性乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)感染的 SD 大鼠的炎症
Authors Zhan WL, Kang YH, Chen N, Mao CS, Kang Y, Shang J
Received 21 August 2017
Accepted for publication 14 September 2017
Published 10 October 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 2947—2955
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S149623
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Junhua Mai
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Abstract: The hepatitis B virus (HBV) has caused acute and chronic liver diseases
in ~350 million infected people worldwide. Halofuginone (HF) is a plant
alkaloid which has been demonstrated to play a crucial role in immune
regulation. Our present study explored the function of HF in the immune
response of HBV-infected Sprague Dawley (SD) rats. Plasmid containing
pCDNA3.1-HBV1.3 was injected in SD rats for the construction of an acute
HBV-infected animal model. Our data showed that HF reduced the high
concentrations of serum hepatitis B e-antigen, hepatitis B surface antigen, and
HBV DNA induced by HBV infection. HF also reduced the number of T helper (Th)17
cells and the expression of interleukin (IL)-17 compared with the
pCDNA3.1-HBV1.3 group. Moreover, pro-inflammatory cytokine levels (IL-17,
IL-23, interferon-γ, and IL-2) were downregulated and anti-inflammatory
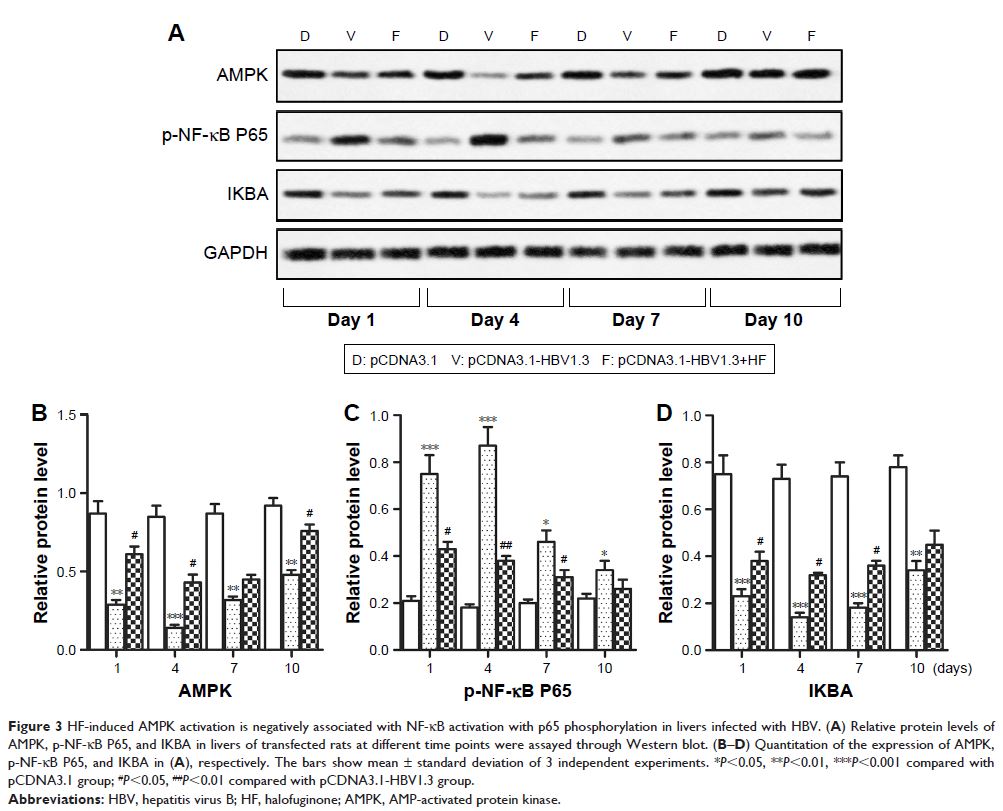
cytokine levels (IL-4 and IL-13) were upregulated by HF. Through further research we found that the expression of AMP-activated
protein kinase (AMPK) and IKBA which suppressed NF-κB activation was increased
while the expression of p-NF-κB P65 was decreased in pCDNA3.1-HBV1.3+HF group
compared with pCDNA3.1-HBV1.3 group, indicating that HF may work through the
activation of AMPK. Finally, our conjecture was further verified by using the
AMPK inhibitor compound C, which counteracted the anti-inflammation effect of
HF, resulting in the decreased expression of AMPK, IKBA and increased
expression of p-NF-κB P65 and reduced number of Th17 cells. In our present
study, HF was considered as an anti-inflammatory factor in acute HBV-infected
SD rats and worked through AMPK-mediated NF-κB p65 inactivation. This study
implicated HF as a potential therapeutic strategy for hepatitis B.
Keywords: halofuginone, hepatitis B virus, inflammation,
AMPK