108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

NEAT1 通过 miR-34a-5p/BCL2 调节卵巢癌的细胞增殖和凋亡
Authors Ding N, Wu H, Tao T, Peng E
Received 23 May 2017
Accepted for publication 28 July 2017
Published 6 October 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 4905—4915
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S142446
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background: Nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) has been demonstrated to act
as a tumor inhibitor in many cancers. However, the role of NEAT1 in the
development of ovarian cancer (OC) remains far from being elaborated. Hence,
the aim of this study is to investigate the expression and function of NEAT1 in
OC.
Materials and
methods: The expression level of NEAT1 was
determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in OC cell
lines. MTT assay, caspase-3 activity assay, and flow cytometry analysis were
conducted to investigate the effects of NEAT1, miR-34a-5p, or B-cell lymphoma-2
(BCL2) on OC cell proliferation and apoptosis. Luciferase reporter assay was
used to confirm the interaction of NEAT1, BCL2, and miR-34a-5p in OC cells.
Results: NEAT1 was significantly upregulated in OC cell lines. NEAT1
overexpression promoted proliferation by increasing the proportion of cells in
S phase and suppressed apoptosis of OC cells, while knockdown of NEAT1 had the
opposite effect. In addition, NEAT1 was demonstrated to directly interact with
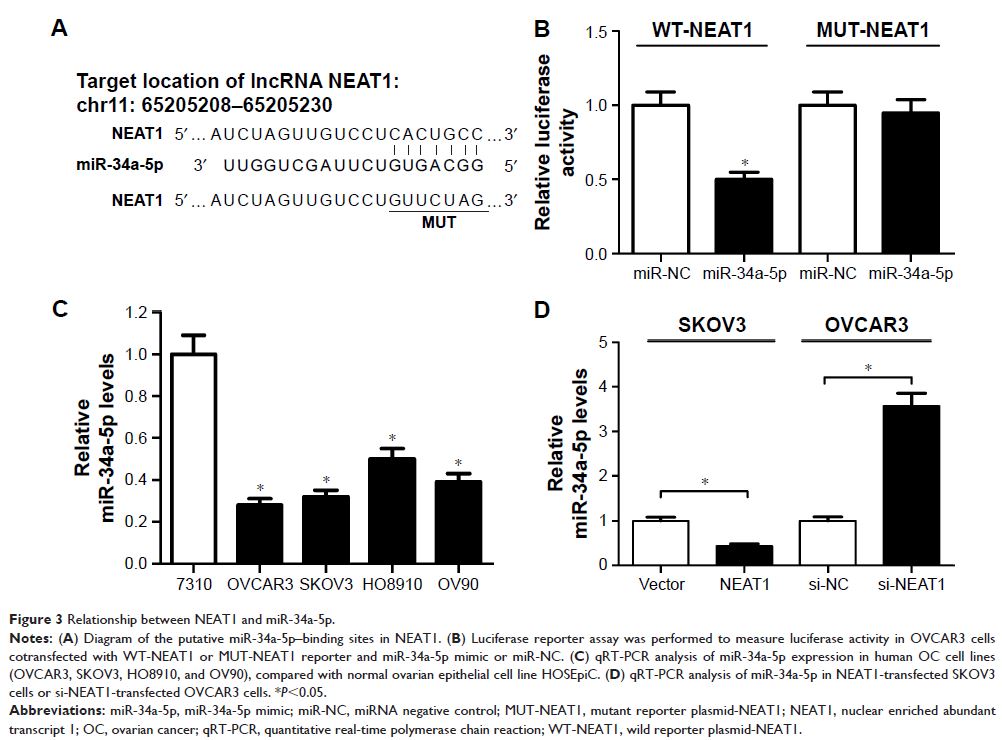
miR-34a-5p and exert its oncogenic role in OC by negatively regulating
miR-34a-5p. Moreover, miR-34a-5p could directly target BCL2 and suppressed its
expression. miR-34a-5p overexpression suppressed OC cell proliferation and
triggered apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Furthermore, NEAT1 knockdown suppressed
BCL2 expression, while anti-miR-34a-5p dramatically abated the inhibitory
effect of si-NEAT1 on BCL2 expression.
Conclusion: NEAT1 regulated proliferation and apoptosis of OC cells by
miR-34a-5p/BCL2, providing a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment
of OC patients.
Keywords: NEAT1, miR-34a-5p, BCL2, ovarian cancer, caspase-3, ceRNA