109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

临床数据与放射学检查相结合可提高胰体腺和胰尾癌 TNM 分期的准确性
Authors Xu W, Jiang B, Yin X
Received 19 April 2017
Accepted for publication 30 August 2017
Published 4 October 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1711—1721
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S139938
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Purpose: Pancreatic body and tail adenocarcinoma (PBTA) remains one of the
deadliest cancers, and current radiological modalities still have limitations
on the staging of PBTA. Improving PBTA staging will contribute to the
management of this disease.
Patients and methods: Clinicopathological characteristics of 91 surgically
treated PBTA patients were retrospectively retrieved. Clinical data associated
with postoperative tumor staging (pTNM) were assessed using ordinal logistic
regression model. Discriminant analysis was performed using function formula
based on multivariate analysis results; further cross-validation was conducted
by Bootstrap methods.
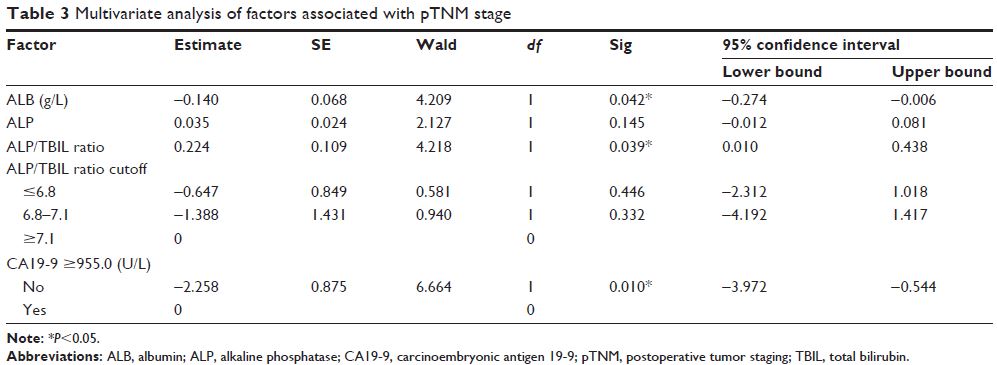
Results: Multivariate analysis showed that carbohydrate
antigen 19-9 ≥955.0 U/L, albumin, and alkaline phosphatase/total bilirubin
ratio were independent factors contributing to improved accuracy of pTNM
staging. Discriminant analysis exhibited better performance and showed that the
probability of accurate prediction of pTNM stage was 90.6% and the probability
of cross-validation was 85.9%. After excluding patients with preoperative
diagnosis of stage IV disease, the probability of accurate prediction of
pTNM stage was 86.1% and the probability of cross-validation was 75.0%.
Conclusion: The combination of imaging and clinical data has
higher accuracy in staging PBTA than radiological data alone. A model proposed
in this study will improve the management of PBTA.
Keywords: pancreatic
cancer, pancreatic body and tail adenocarcinoma, TNM staging, diagnostic
imaging