108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-190a-5p 的通过靶向 SLC17A6 起到抑制糖尿病性神经性疼痛的作用
Authors Yang D, Yang Q, Wei X, Liu Y, Ma D, Li J, Wan Y, Luo Y
Received 2 February 2017
Accepted for publication 20 April 2017
Published 4 October 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 2395—2403
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S133755
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
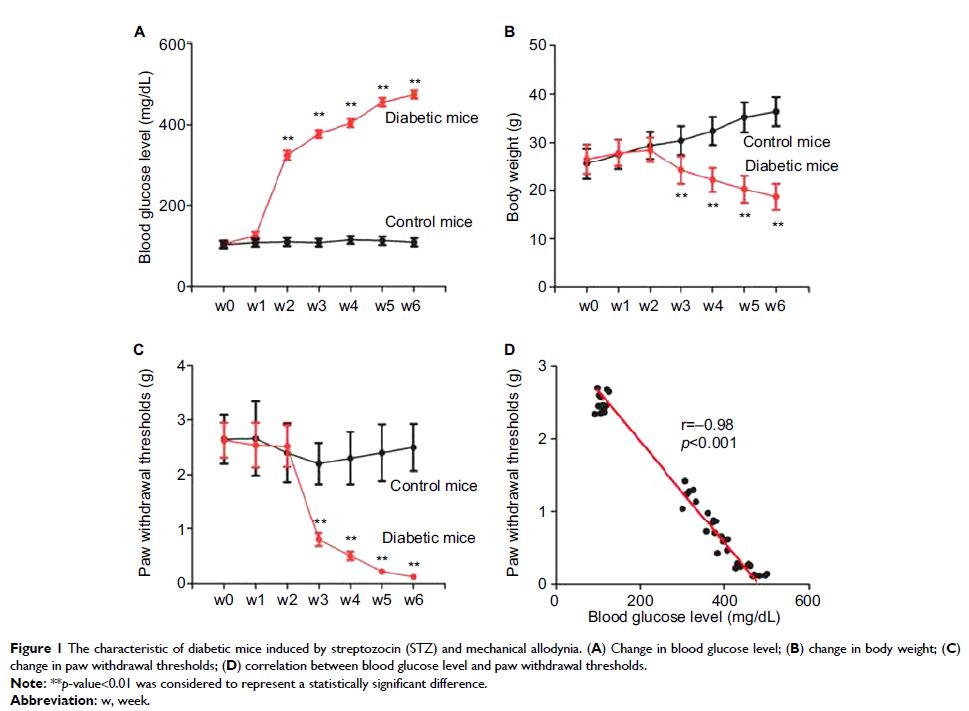
Introduction: MicroRNAs play a key
role in neuropathic pain. In a previous study, miR-190a-5p was significantly
downregulated in diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP). However, the role and
pathological mechanism of miR-190a-5p in DNP still remain unclear.
Materials and methods: DNP model was established. The paw withdrawal
thresholds were measured to assess the mechanical nociceptive response.
Dual-luciferase reporter assay was used to confirm the target gene of microRNA.
The expressions of microRNA, gene, and protein were detected by the
quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction or Western blot. The levels of
IL-1β and IL-6 were detected with the enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay.
Results: Compared with the control sample, the expression
of miR-190a-5p was decreased and SLC17A6 was increased in the spinal tissue
from those developing DNP. The bioinformatics and luciferase reporter assay
demonstrated that SLC17A6 is a direct target of miR-190a-5p. Up-regulation of
miR-190a-5p and inhibition of SLC17A6 could significantly weaken the painful
behavior and reduce IL-1β and IL-6 level in DNP.
Conclusion: miR-190a-5p is involved in DNP via targeting
SLC17A6, and miR-190a-5p and SLC17A6 may be the therapeutic targets of this
disease.
Keywords: miR-190a-5p,
DNP, spinal tissue, painful behavior, IL-1β and IL-6, SLC17A66