109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Observation and Interview-based Diurnal Sleepiness Inventory for measurement of sleepiness in older adults
Authors Pak VM, Onen SH, Gooneratne NS, Falissard B, Onen F
Received 7 February 2017
Accepted for publication 9 August 2017
Published 29 September 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 241—247
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NSS.S134112
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Steven Shea
Introduction: There
is no established reference standard for subjective measures of sleepiness in
older adults.
Methods: This study compares the Observation and Interview-based Diurnal
Sleepiness Inventory (ODSI) with two existing instruments for measurement of
sleepiness and daily functioning, the Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS) and
Functional Outcomes of Sleep Questionnaire (FOSQ).
Results: A total of 125 study participants were included in this study and
were administered the ODSI, ESS and FOSQ; subjects had a mean age of 70.9 ±
5.27 years, mean Apnea–Hypopnea Index of 31.9 ± 27.9 events/hour and
normal cognitive functioning (Mini-Mental State Examination score > 24). The
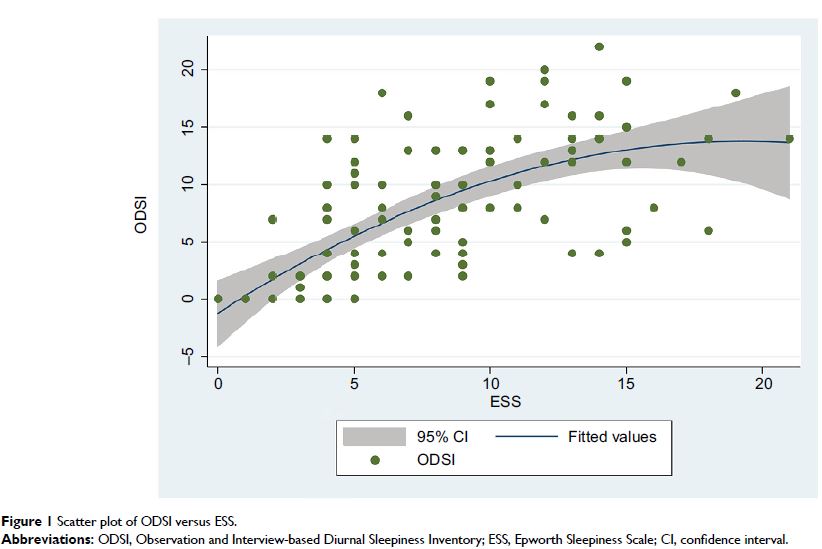
ODSI showed a significant association with the ESS (Spearman’s ρ: 0.67, P < 0.001) and with the
FOSQ (Spearman’s ρ: –0.52, P < 0.001).
The ODSI 1 item (assessing sleepiness in active situations) was borderline
significantly correlated with the ESS (β = 0.14; 95% confidence interval [CI],
–0.01 to 0.29; P = 0.069).
ODSI 2 item (sleepiness in passive situations) was correlated with the ESS (β =
1.65; 95% CI, 1.32 to 1.98; P < 0.001).
Both ODSI 1 (β = –0.15; 95% CI, –0.24 to –0.07; P < 0.001) and ODSI 2 (β =
–0.35; 95% CI, –0.55 to 0.16; P < 0.001)
were significantly correlated with the FOSQ.
Conclusion: The ODSI is a suitable measure of sleepiness and is appropriate for
usage in clinical care in older adults.
Keywords: excessive daytime sleepiness, functional status, sleep disorders,
questionnaires