108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

归因于风湿性痛风的腰痛性脊柱狭窄:病例报告和文献综述
Authors Wang W, Li QB, Cai L, Liu WJ
Received 9 July 2017
Accepted for publication 24 August 2017
Published 28 September 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1287—1293
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S145906
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Objectives: Tophaceous
gout seldom affects the axial skeleton. Symptoms vary according to the
differential localization of urate deposits and the diagnosis is often delayed.
Here, we report an unusual case of lumbar spinal stenosis caused by extradural
tophaceous deposits.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed a case of a patient with tophaceous
gout of the lumbar spine and reviewed the relevant literature.
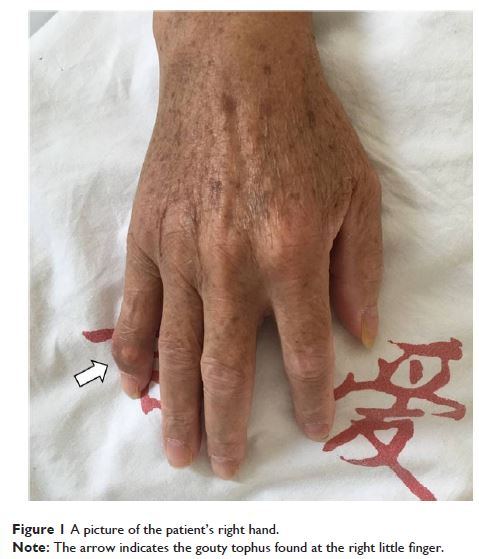
Results: A 62-year-old man with a 2-year history of lower back pain and a 3-month
history of lower limb radiation pain and intermittent claudication was
admitted. After laboratory and imaging investigations he underwent surgical
decompression and stabilization. Histological analysis of the extracted
specimen confirmed that it was gouty tophus. The patient’s symptoms improved
progressively after the operation. He recovered very well with no
complications.
Conclusion: The mechanism associated with axial gout is not yet clear. Obesity,
inactivity, and previous degenerative disc disease may be the risk factors for
spinal tophus. The clinical symptoms are diverse according to the differential
localization of urate deposits. It is not easy to diagnose this disease
radiographically by routine radiological examination. Analysis of a biopsy
specimen is definitely the only way to confirm diagnosis. Surgical treatment
should be considered in patients with spinal gout who are experiencing
neurological deterioration.
Keywords: tophaceous gout, spinal gout, case report