108985
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

青蒿琥酯 (Artesunate) 可防止大鼠发生氯氮平 (clozapine) 诱导的肝脂肪变性和血浆甘油三酯升高
Authors Li Y, Su R, Xu S, Huang Q, Xu H
Received 28 June 2017
Accepted for publication 17 August 2017
Published 27 September 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 2477—2487
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S145069
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Roger Pinder
Abstract: Clozapine is an atypical antipsychotic with therapeutic efficacy
in treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients and low incidence of
extrapyramidal side effects. However, the use of clozapine has been limited by
its adverse effects on metabolism. Artesunate is a semisynthetic derivative of
artemisinin and was shown to decrease the plasma cholesterol and triglyceride
in rabbits and rats in recent studies. The aim of this study was to examine
possible effects of artesunate on the clozapine-induced metabolic alterations
in rats given saline, clozapine, artesunate, or clozapine plus artesunate for 6
weeks. The clozapine group showed significantly high plasma levels of
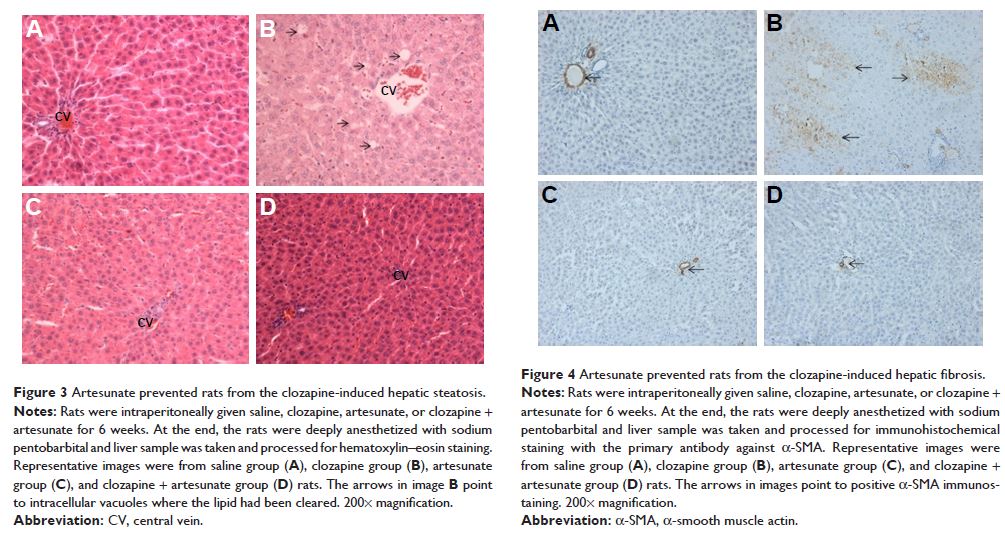
triglyceride, hepatic steatosis, and fibrosis along with high levels of
C-reactive protein, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase
compared to the saline group. But the treatment had no effect on weight gain
and caused no hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and behavioral changes in the
rats. More significantly, these clozapine-induced changes were not seen in rats
coadministered with clozapine plus artesunate. These results added evidence
supporting psychiatrists to try add-on treatment of artesunate in schizophrenia
patients to ameliorate clozapine-induced adverse metabolic effects.
Keywords: artesunate,
clozapine, dyslipidemia, hepatic steatosis, schizophrenia