109182
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

NanoVelcro 捕获的 CTC 数量随着 MMP7 和 MMP9 的血清水平升高而增加,因而可准确预测肺腺癌患者的转移和预后不良
Authors Sun Y, Chen Y, Li S, Lei Y, Xu D, Jiang N, Zhang Y, Cao J, Ke Z
Received 15 June 2017
Accepted for publication 28 July 2017
Published 31 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 6399—6412
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S144033
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Dongwoo Khang
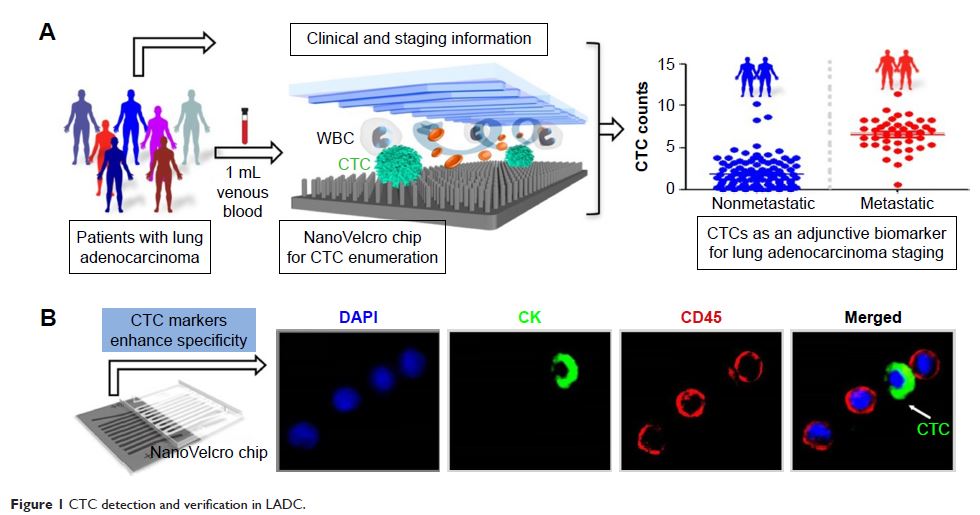
Abstract: Lung
adenocarcinoma (LADC) is among the most malignant cancers that frequently develops
micrometastases even in early stages of the disease. Circulating tumor cell
(CTC) number, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 7, and MMP9 show great prospects
as predictive biomarkers in many tumors. However, the interactions between
these biomarkers and the molecular basis of their roles in the metastasis and
prognosis of LADC remain unclear. The present study revealed that an elevated
CTC count and overexpression of MMP7 and MMP9 correlate with metastasis and
clinical progression in LADC patients (n=143). Furthermore, MMP7 and MMP9
upregulation facilitates LADC cell migration in vitro and enhances serum CTC
levels in a xenograft mouse model. More importantly, receiver operating
characteristic (ROC) curves and Kaplan–Meier analysis confirmed more accurate
prediction of metastasis and overall survival (OS) with a combination panel of
CTC, MMP7, and MMP9. Taken together, our data show, for the first time, the
involvement of MMP7 and MMP9 in the release of CTCs into the peripheral blood,
and our data reveal that CTC count and expression of MMP7 and MMP9 can be used
together as an effective clinical prediction panel for LADC metastasis and
prognosis.
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, circulating tumor cell, MMP7/MMP9,
metastasis, prognosis