109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

姜黄素 (Curcumin) 通过调节 Bax/Bcl-2 表达来抑制凋亡并减轻链脲佐菌素 (streptozotocin) 诱导的糖尿病大鼠睾丸的氧化应激
Authors Zhao L, Gu Q, Xiang L, Dong X, Li H, Ni J, Wan L, Cai G, Chen G
Received 13 May 2017
Accepted for publication 28 July 2017
Published 28 August 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1099—1105
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S141738
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Hoa Le
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Scope: The present study was designed to examine the damage caused by
high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetes on the testis of rats and the
effects of curcumin against oxidative stress and apoptosis from high-fat diet
and diabetes.
Methods: Diabetes was induced by intraperitoneal
injection of streptozotocin (30 mg/kg in 0.1 M sodium citrate buffer, pH
4.5) in obese rats. The rats in the obese and diabetic groups were treated with
a daily dose of curcumin by intragastric intubation (100 mg/kg body
weight) for 8 weeks. Testis tissue sections were stained with
hematoxylin–eosin, and apoptosis was identified in situ by using terminal
deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling.
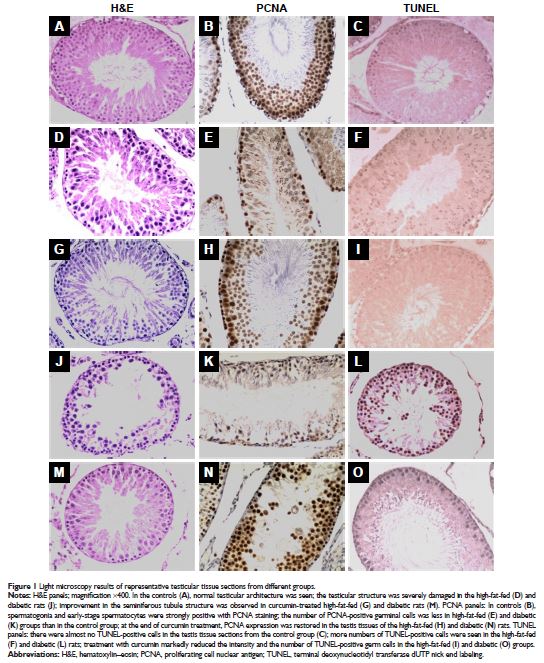
Results: Curcumin treatment improved the histological
appearance of the testis and significantly reduced the apoptosis level in the
testicular cells of the obese and the diabetic rats. The expression of
proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) was restored in the testis tissues of
diabetic rats at the end of curcumin treatment. Molecular analysis demonstrated
that curcumin treatment significantly and simultaneously decreased Bax and
increased Bcl-2 expressions, therefore elevating the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax.
Furthermore, curcumin treatment significantly decreased malondialdehyde (MDA)
and increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels in testis tissue samples of the
diabetic rats.
Conclusion: Curcumin treatment preserved the morphology of testes;
restored the expression of PCNA, MDA, and SOD; and inhibited testicular cell
death in diabetic rats. The capability of curcumin in inhibiting oxidative
stress and modulating the Bax/Bcl-2-mediated cell death pathway reveals its
potential as a therapeutic agent against diabetes.
Keywords: apoptosis,
curcumin, diabetes, oxidative stress, testis