109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

包覆佐剂枸杞 (Lycium barbarum ) 多糖的简单纳米脂质体可改善小鼠的体液和细胞免疫
Authors Bo R, Sun Y, Zhou S, Ou N, Gu P, Liu Z, Hu Y, Liu J, Wang D
Received 12 March 2017
Accepted for publication 8 August 2017
Published 28 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 6289—6301
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S136820
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Dongwoo Khang
Abstract: The
success of subunit vaccines has been hampered by the problems of weak or
short-term immunity and the lack of availability of nontoxic, potent adjuvants.
It would be desirable to develop safe and efficient adjuvants with the aim of
improving the cellular immune response against the target antigen. In this
study, the targeting and sustained release of simple nanoliposomes
containing Lycium barbarum polysaccharides
(LBP) as an efficacious immune adjuvant to improve immune responses were
explored. LBP liposome (LBPL) with high entrapment efficiency (86%) were
obtained using a reverse-phase evaporation method and then used to encapsulate
the model antigen, ovalbumin (OVA). We demonstrated that the as-synthesized
liposome loaded with OVA and LBP (LBPL-OVA) was stable for 45 days and
determined the encapsulation stability of OVA at 4°C and 37°C and the release
profile of OVA from LBPL-OVA was investigated in pH 7.4 and pH 5.0. Further in
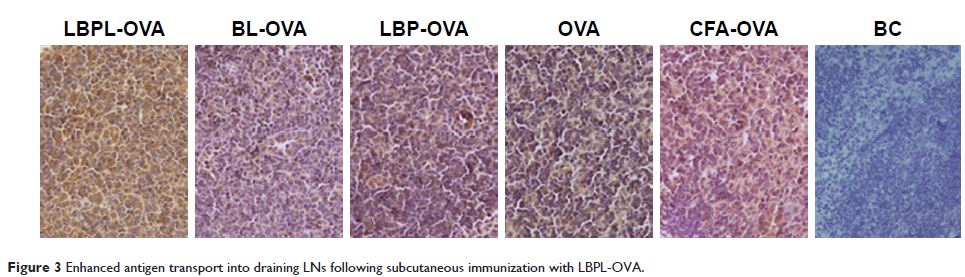
vivo investigation showed that the antigen-specific humoral response was correlated
with antigen delivery to the draining lymph nodes. The LBPL-OVA were also
associated with high levels of uptake by key dendritic cells in the draining
lymph nodes and they efficiently stimulated CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proliferation in vivo, further
promoting antibody production. These features together elicited a significant
humoral and celluar immune response, which was superior to that produced by
free antigen alone.
Keywords: Lycium barbarum polysaccharide
liposome, adjuvant, ovalbumin, draining lymph nodes, antigen-specific humoral
response