108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过抑制无嘌呤/无嘧啶核酸内切酶 1-激活的 IL-6/STAT3 信号通路,以 AT-101 进行序贯疗法提高人体非小细胞性肺癌细胞的顺铂化学敏感性
Authors Ren T, Shan J, Qing Y, Qian C, Li Q, Lu G, Li M, Li C, Peng Y, Luo H, Zhang S, Zhang W, Wang D, Zhou SF
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2014:8 Pages 2517—2529
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S71432
Received 20 July 2014, Accepted 2 September 2014, Published 12 December 2014
Abstract: AT-101,
known as R-(–)-gossypol, is a potent anticancer agent, but its chemosensitizing
effects remain elusive. The present study aimed to examine whether AT-101 could
increase the sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells to cisplatin
(CDDP) and the underlying mechanisms. We evaluated the efficacy of the
sequential treatment with AT-101 and CDDP using both in vitro and in vivo
models. Our results showed that as compared to AT-101 or CDDP monotherapy, or
AT-101 plus CDDP concurrent treatment, the sequential treatment significantly
inhibited cell proliferation and migration and induced tumor cell death.
Moreover, the efficacy of the sequential treatment was also confirmed in a
mouse A549 xenograft model. Our study revealed that AT-101 inhibited the
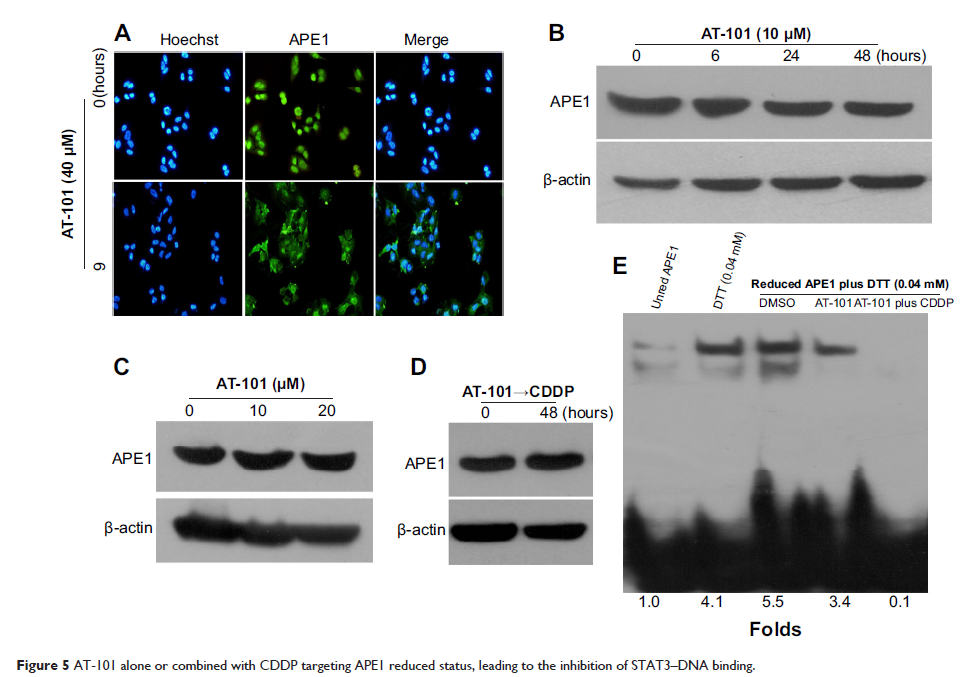
reduced status of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) and attenuated
APE1-mediated IL-6/STAT3 signaling activation by decreasing IL-6 protein
expression; suppressing the STAT3–DNA binding; and reducing the expression of
the downstream antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. In conclusion, AT-101
enhances the sensitivity of A549 cells to CDDP in vitro and in vivo through the
inhibition of APE1-mediated IL-6/STAT3 signaling activation, providing a
rationale for the combined use of AT-101 and CDDP in non-small cell lung cancer
chemotherapy.
Keywords: AT101, NSCLC,
cisplatin, chemosensitivity, APE1, STAT3, nude mice, apoptosis