108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
基于 H37Rv 绑定肽使用表面功能化磁性微球配以量子点检测结核分歧杆菌 —结核杆菌纳米探测法
Authors Yang H, Qin L, Wang Y, Zhang B, Liu Z, Ma H, Lu J, Huang X, Shi D, Hu Z
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2015:10 Pages 77—88
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S71700
Received 24 July 2014, Accepted 15 October 2014, Published 17 December 2014
Abstract: Despite suffering from the major disadvantage of low sensitivity,
microscopy of direct smear with the Ziehl–Neelsen stain is still broadly used
for detection of acid-fast bacilli and diagnosis of tuberculosis. Here, we
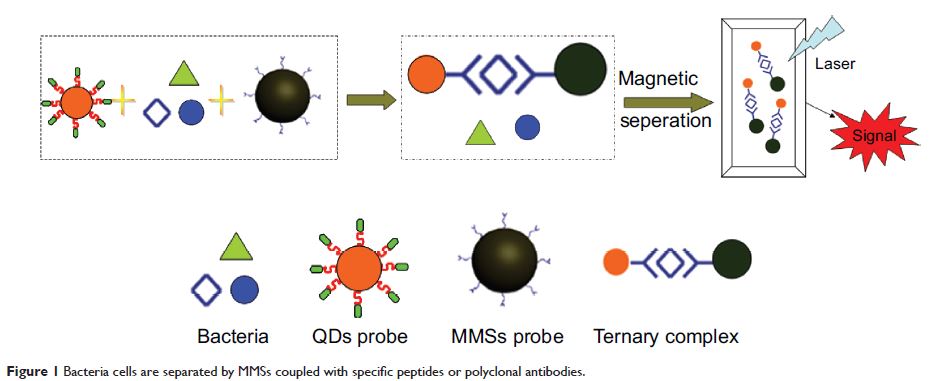
present a unique detection method of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) using surface functionalized magnetic microspheres (MMSs) coupled with
quantum dots (QDs), conjugated with various antibodies and phage
display-derived peptides. The principle is based upon the conformation of the
sandwich complex composed of bacterial cells, MMSs, and QDs. The complex system
is tagged with QDs for providing the fluorescent signal as part of the
detection while magnetic separation is achieved by MMSs. The peptide ligand H8
derived from the phage display library Ph.D.-7 is developed for MTB cells.
Using the combinations of MMS-polyclonal antibody+QD-H8 and MMS-H8+QD-H8, a
strong signal of 103 colony forming units (CFU)/mL H37Rv was obtained with improved specificity. MS-H8+QD-H8 combination was further
optimized by adjusting the concentrations of MMSs, QDs, and incubation time for
the maximum detection signal. The limit of detection for MTB was found to reach
103 CFU/mL even for the sputum matrices. Positive sputum samples
could be distinguished from control. Thus, this novel method is shown to
improve the detection limit and specificity of MTB from the sputum samples, and
to reduce the testing time for accurate diagnosis of tuberculosis, which needs
further confirmation of more clinical samples.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis , phage display, binding peptides, magnetic microspheres, quantum dots, detection
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis , phage display, binding peptides, magnetic microspheres, quantum dots, detection