109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

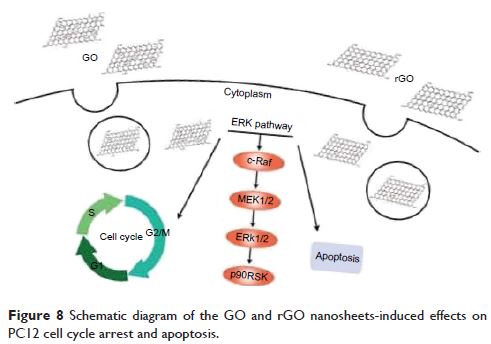
氧化石墨烯 (Graphene) 和还原氧化石墨烯可通过 ERK 信号通路诱导神经性嗜铬细胞瘤衍生的 PC12 细胞系凋亡和细胞周期改变
Authors Kang YY, Liu J, Wu JR, Yin Q, Liang HM, Chen AJ, Shao LQ
Received 3 May 2017
Accepted for publication 6 July 2017
Published 2 August 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5501—5510
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S141032
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Given the novel
applications of graphene materials in biomedical and electronics industry, the
health hazards of these particles have attracted extensive worldwide attention.
Although many studies have been performed on graphene material-induced toxic
effects, toxicological data for the effect of graphene materials on the nervous
system are lacking. In this study, we focused on the biological effects of
graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) materials on PC12 cells, a
type of traditional neural cell line. We found that GO and rGO exerted
significant toxic effects on PC12 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner.
Moreover, apoptosis appeared to be a response to toxicity. A potent increase in
the number of PC12 cells at G0/G1 phase after GO and rGO exposure was detected
by cell cycle analysis. We found that phosphorylation levels of ERK signaling
molecules, which are related to cell cycle regulation and apoptosis, were
significantly altered after GO and rGO exposure. In conclusion, our results
show that GO has more potent toxic effects than rGO and that apoptosis and cell
cycle arrest are the main toxicity responses to GO and rGO treatments, which
are likely due to ERK pathway regulation.
Keywords: graphene oxide,
reduced graphene oxide, PC12, cell cycle alterations, ERK pathway