109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在同步放化疗中加入诱导化疗治疗 T3N0-1 期鼻咽癌:一个倾向值匹配研究
Authors Lan XW, Xiao Y, Zou XB, Zhang XM, OuYang PY, Xie FY
Received 4 February 2017
Accepted for publication 3 May 2017
Published 1 August 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3853—3860
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S133917
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Objective: Our objective was to examine whether adding induction chemotherapy
to concurrent chemoradiotherapy improved survival in stage III nasopharyngeal
carcinoma (NPC) patients, especially in low-risk patients at stage T3N0-1.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analyzed 687 patients with
stage T3N0-1 NPC treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) plus
concurrent chemotherapy (CC) with or without induction chemotherapy (IC).
Propensity score matching (PSM) method was used to select 237 pairs of patients
from two cohorts. Overall survival (OS), locoregional relapse-free survival
(LRFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), and progression-free survival
(PFS) were assessed by using the Kaplan–Meier method, log-rank test, and Cox
regression analysis.
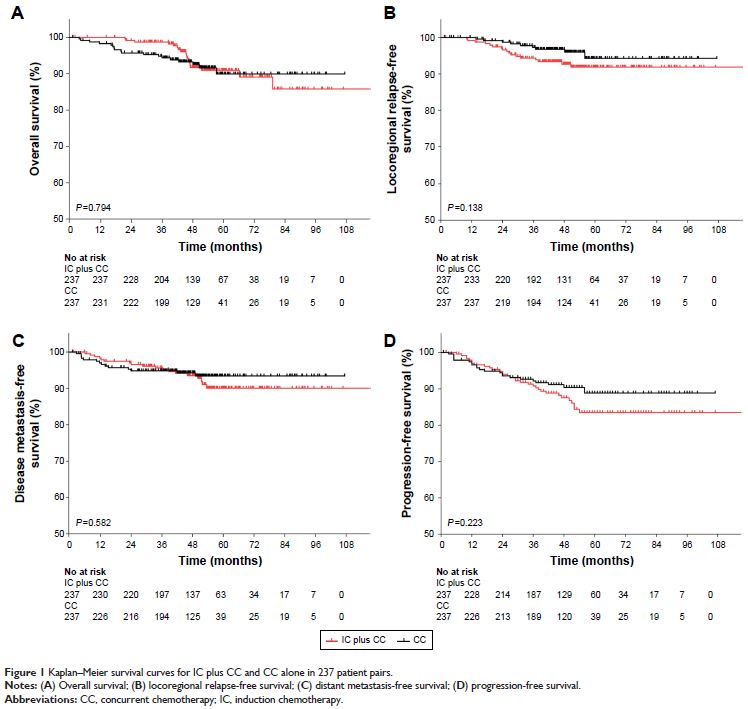
Results: No significant survival differences were
observed between IC plus CC and CC cohorts with similar 4-year OS (91.7% vs
92.6%, P =0.794), LRFS, (92.7% vs
96.8%, P =0.138), DMFS (93.5% vs
94.3%, P =0.582), and PFS (87.5% vs
91.1%, P =0.223). In a univariate
analysis, lower Epstein–Barr virus deoxyribonucleic acid (EBV DNA; <4,000
copies/mL) significantly improved 4-year DMFS (95.5% vs 91.6%, P =0.044) compared with higher EBV
DNA (≥4,000 copies/mL). No factors were associated with 4-year OS, LRFS,
DMFS, and PFS in a multivariate analysis. IC plus CC group experienced higher
rates of grade 3–4 leucopenia (P <0.001) and
neutropenia (P <0.001).
Conclusion: The addition of IC to CC in stage T3N0-1 NPC patients
treated with IMRT did not significantly improve their survival. The IC group
experienced higher rates of grade 3–4 hematological toxicities. Therefore,
further investigation is required.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal
carcinoma, induction chemotherapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy,
propensity score matching, stage T3N0-1