109229
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
介孔硅酸镁掺入聚(ε - 己内酯) - 聚(乙二醇) - 聚(ε - 己内酯)的生物活性复合物有利成骨细胞的行为
Authors Niu Y, Dong W, Guo H, Deng Y, Guo L, An X, He D, Wei J, Li M
Published Date May 2014 Volume 2014:9(1) Pages 2665—2675
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S59040
Received 11 December 2013, Accepted 7 February 2014, Published 27 May 2014
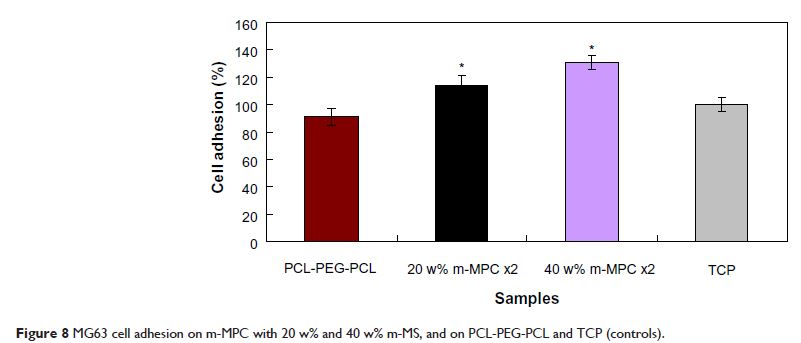
Abstract: Mesoporous magnesium silicate (m-MS) and poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL-PEG-PCL) composite (m-MPC) was synthesized by solvent casting method. The results suggest that the mechanical properties of compressive strength and elastic modulus, as well as hydrophilicity, of the m-MPC increased with increase of m-MS content in the composites. In addition, the weight loss of the m-MPC improved significantly with the increase of m-MS content during composite soaking in phosphate-buffered saline for 10 weeks, indicating that incorporation of m-MS into PCL-PEG-PCL could enhance the degradability of the m-MPC. Moreover, the m-MPC with 40 w% m-MS could induce a dense and continuous apatite layer on its surface after soaking in simulated body fluid for 5 days, which was better than m-MPC 20 w% m-MS, exhibiting excellent in vitro bioactivity. In cell cultural experiments, the results showed that the attachment and viability ratio of MG63 cells on m-MPC increased significantly with the increase of m-MS content, showing that the addition of m-MS into PCL-PEG-PCL could promote cell attachment and proliferation. The results suggest that the incorporation of m-MS into PCL-PEG-PCL could produce bioactive composites with improved hydrophilicity, degradability, bioactivity, and cytocompatibility.
Keywords: PCL-PEG-PCL, degradation, cytocompatibility, cell attachment, cell proliferation
Keywords: PCL-PEG-PCL, degradation, cytocompatibility, cell attachment, cell proliferation