109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

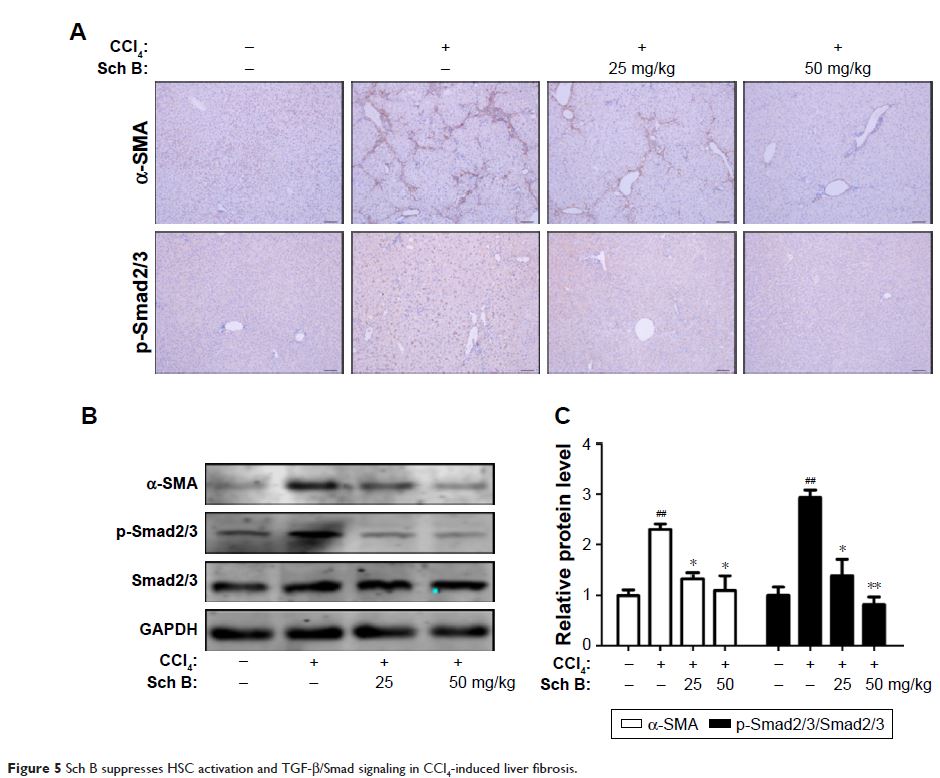
五味子 B (Schisandrin B) 通过调节 Nrf2-ARE 和 TGF-β/Smad 信号通路来减弱大鼠中 CCl4 诱导的肝纤维化
Authors Chen QS, Zhang H, Cao Y, Li Y, Sun S, Zhang JP, Zhang GQ
Received 20 March 2017
Accepted for publication 2 June 2017
Published 26 July 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 2179—2191
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S137507
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Venkateshwar Madka
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Abstract: Liver fibrosis is a major pathological feature of chronic liver
diseases and there is no effective therapy program at present. Schisandrin B
(Sch B) is the major bioactive ingredient of Schisandra
chinensis , with antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and hepatoprotective
properties. This study aimed to investigate the protective effect and related
molecular mechanism of Sch B against carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis in rats. The in vivo
therapeutic effect of Sch B on liver fibrosis induced by CCl4 was examined in rats. In vitro, rat hepatic
stellate cells (HSC-T6) were used to assess the effect of Sch B on the
activation of HSCs. Sch B effectively attenuated liver damage and progression
of liver fibrosis in rats, as evidenced by improved liver function and
decreased collagen deposition. The effects of Sch B were associated with
attenuating oxidative stress by activating nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related
factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated antioxidant signaling and suppressing HSC activation
by inhibiting the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)/Smad signaling pathway.
In an in vitro study, it was shown that Sch B inhibited TGF-β-induced HSC
activation. Finally, Sch B significantly inhibited TGF-β1-stimulated
phosphorylation of Smad and signaling of mitogen-activated protein kinases.
This study demonstrates that Sch B prevents the progression of liver fibrosis
by the regulation of Nrf2-ARE and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways, and indicates
that Sch B can be used for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
Keywords: schisandrin B,
liver fibrosis, hepatic stellate cell activation, Nrf2, TGF-β/Smad