109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

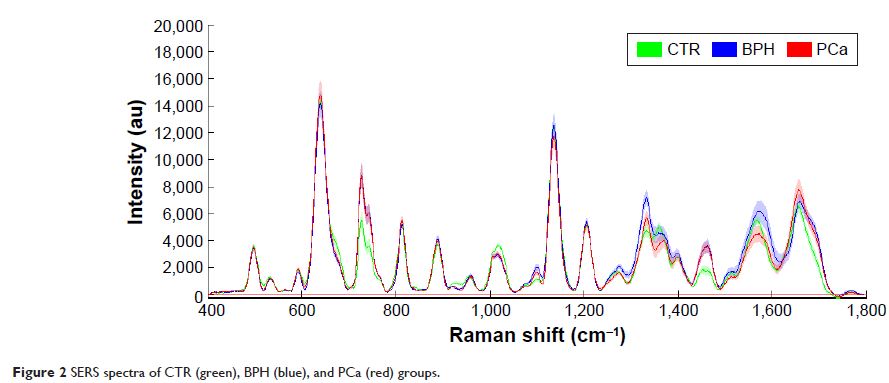
血清的表面增强拉曼光谱 (Raman spectroscopy) 分析可为前列腺特异性抗原水平为 4–10 ng/mL 的患者准确检测前列腺癌
Authors Chen N, Rong M, Shao X, Zhang H, Liu S, Dong B, Xue W, Wang T, Li T, Pan J
Received 23 March 2017
Accepted for publication 23 May 2017
Published 27 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5399—5407
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S137756
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: The
surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) of blood serum was investigated to
differentiate between prostate cancer (PCa) and benign prostatic hyperplasia
(BPH) in males with a prostate-specific antigen level of 4–10 ng/mL, so as
to reduce unnecessary biopsies. A total of 240 SERS spectra from blood serum
were acquired from 40 PCa subjects and 40 BPH subjects who had all received
prostate biopsies and were given a pathological diagnosis. Multivariate
statistical techniques, including principal component analysis (PCA) and linear
discriminant analysis (LDA) diagnostic algorithms, were used to analyze the
spectra data of serum from patients in control (CTR), PCa and BPH groups;
results offered a sensitivity of 97.5%, a specificity of 100.0%, a precision of
100.0% and an accuracy of 99.2% for CTR; a sensitivity of 90.0%, a specificity
of 97.5%, a precision of 94.7% and an accuracy of 98.3% for BPH; a sensitivity
of 95.0%, a specificity of 93.8%, a precision of 88.4% and an accuracy of 94.2%
for PCa. Similarly, this technique can significantly differentiate low- and
high-risk PCa with an accuracy of 92.3%, a specificity of 95% and a sensitivity
of 89.5%. The results suggest that analyzing blood serum using SERS combined
with PCA–LDA diagnostic algorithms is a promising clinical tool for PCa
diagnosis and assessment.
Keywords: Ag nanoparticles, linear discriminant analysis, gray zone,
principle component analysis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, spectral
classification