109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对成纤维细胞激活蛋白 α 敏感并包覆合成尿探测剂的纳米颗粒用于实体瘤诊断
Authors Feng XW, Wang QF, Liao YH, Zhou X, Wang YD, Liu WL, Zhang G
Received 6 April 2017
Accepted for publication 7 June 2017
Published 27 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5359—5372
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S139039
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
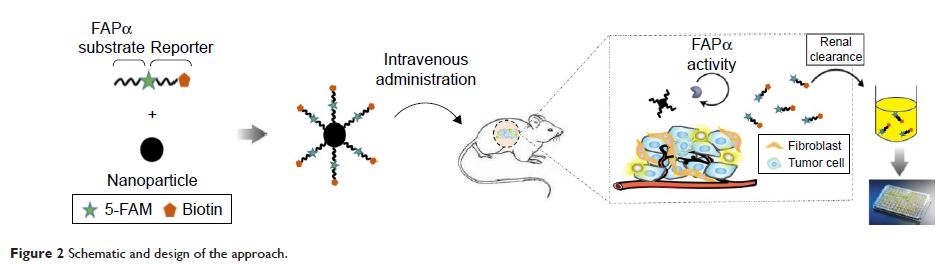
Abstract: We
developed fibroblast activation protein α (FAPα)-sensitive magnetic iron oxide
nanoparticles (MNPs) by conjugating a substrate-reporter tandem peptide as a
synthetic biomarker to the surface of MNPs (marker-MNPs). In vitro, the
marker-MNPs showed stability when treated with serum or urine and exhibited
high susceptibility and specificity for FAPα enzyme and 3T3/FAPα cell line.
Furthermore, the marker-MNPs were administered to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
xenograft tumor mice; they reached the tumor tissues in the mice, where they
were cleaved effectively by the local overexpressed FAPα to release the
reporter peptide and filter it into the urine. The tumor targeting and
biodistribution of marker-MNPs were verified by in vivo imaging. The cleaved
reporter peptides in urine detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay have
high diagnostic accuracy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (area under the
receiver-operating characteristic curve =1.0). Our study implies a promising
strategy of utilizing the low-cost and noninvasive synthetic urinary
probe–coated nanoparticles for the diagnosis of FAPα-positive solid tumors,
except for in renal cancer.
Keywords: synthetic urinary probe, magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles, fibroblast
activation protein α, tumor diagnosis