109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

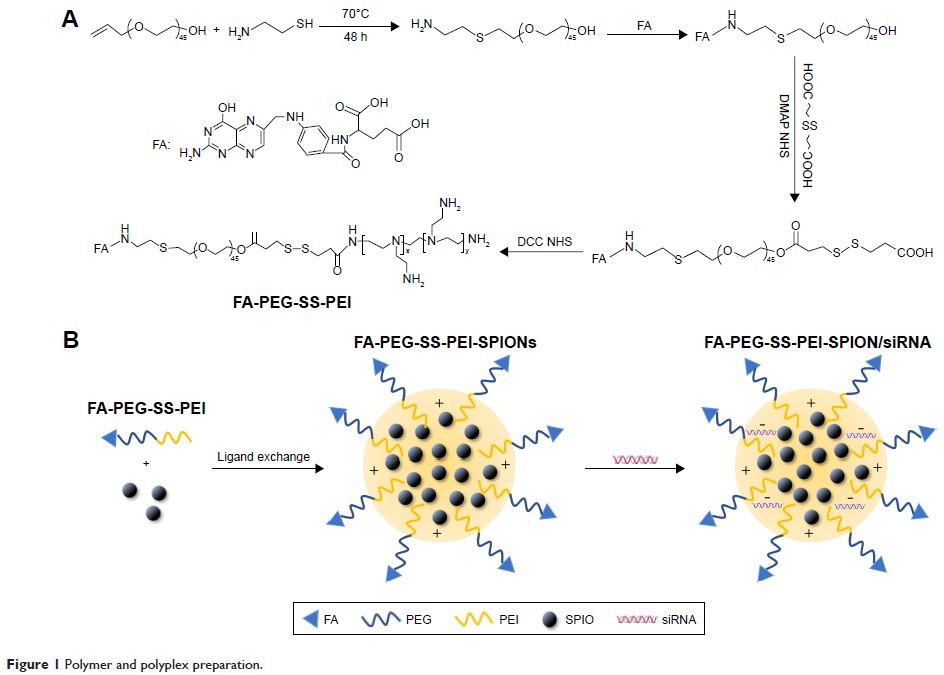
叶酸官能化的聚乙烯亚胺 (Polyethylenimine) 超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子作为磁共振成像诊断造影剂,以及 PD-L1 siRNA 递送治疗胃癌
Authors Luo X, Peng X, Hou J, Wu S, Shen J, Wang L
Received 16 March 2017
Accepted for publication 23 May 2017
Published 26 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5331—5343
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S137245
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Eytan Klausner
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1), which is highly expressed in gastric
cancers, interacts with programmed death-1 (PD-1) on T cells and is involved in
T-cell immune resistance. To increase the therapeutic safety and accuracy of
PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, RNA interference through targeted gene delivery was
performed in our study. We developed folic acid (FA)- and disulfide
(SS)–polyethylene glycol (PEG)-conjugated polyethylenimine (PEI) complexed with
superparamagnetic iron oxide Fe3O4 nanoparticles (SPIONs) as a siRNA-delivery system
for PD-L1 knockdown. The characterization, binding ability, cytotoxicity,
transfection efficiency, and cellular internalization of the polyplex were
determined. At nitrogen:phosphate (N:P) ratios of 10 or above, the
FA-PEG-SS-PEI-SPIONs bound to PD-L1 siRNA to form a polyplex with a diameter of
approximately 120 nm. Cell-viability assays showed that the polyplex had
minimal cytotoxicity at low N:P ratios. The FA-conjugated polyplex showed
higher transfection efficiency and cellular internalization in the folate
receptor-overexpressing gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901 than a
non-FA-conjugated polyplex. Subsequently, we adopted the targeted
FA-PEG-SS-PEI-SPION/siRNA polyplexes at an N:P ratio of 10 for function
studies. Cellular magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed that the polyplex
could also act as a T 2-weighted contrast agent for cancer MRI.
Furthermore, one of four PD-L1 siRNAs exhibited effective PD-L1 knockdown in
PD-L1-overexpressing SGC-7901. To determine the effects of the functionalized
polyplex on T-cell function, we established a coculture model of activated T
cells and SGC-7901 cells and demonstrated changes in secreted cytokines. Our
findings highlight the potential of this class of multifunctional theranostic
nanoparticles for effective targeted PD-L1-knockdown therapy and MRI diagnosis
in gastric cancers.
Keywords: magnetic
resonance imaging, theranostics, RNA interference, PEI, cellular
internalization